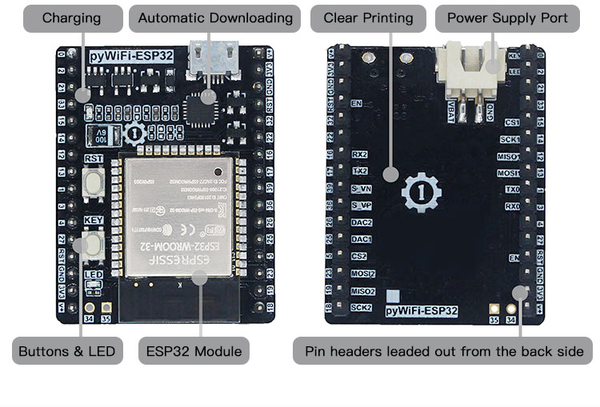
pyWiFi-ESP32 Development Board Kit Development Board
Code name: ESP32_DEV
pyWiFi-ESP32 Development Board Kit development board is based on esp32 microcontroller and uses xtensa architecture. This board has a maximum CPU frequency of 240 MHz and a flash size of 4MB.
About pyWiFi-ESP32 Development Board Kit
The pyWiFi-ESP32 is a comprehensive development kit based on the ESP32 microcontroller, designed for MicroPython programming and IoT applications. It features integrated Wi-Fi 802.11 b/g/n and Bluetooth 4.2 + BLE for wireless connectivity. 📶
Powered by a dual-core Xtensa 32-bit LX6 processor at up to 240 MHz, with 4MB flash memory and 520KB SRAM, it's ideal for IoT projects, home automation, and educational purposes. ⚡
The kit includes a variety of sensors: Atmospheric Pressure Sensor, Water Level Sensor, Soil Humidity Sensor, Ultrasonic Sensor, Human Infrared Sensor, and Photosensitive Sensor. It also comes with a pyBase expansion board, 0.96" OLED display, and Micro USB cable. 🔌
Operating at 3.3V with power input from 3.6V to 6V (recommended USB 5V), and 3.3V output up to 600mA. Features an onboard LED connected to GPIO2 and a button on GPIO0. Supports I2C and PWM on any GPIO pin. 🔋
Where to Buy pyWiFi-ESP32 Development Board Kit


Prices are subject to change. We earn from qualifying purchases as an Amazon Associate.
pyWiFi-ESP32 Development Board Kit Technical Specifications
🔌 USB
🛰️ Connectivity
🧠 Microcontroller
✨ Features
- 30 digital IO pins
- 16 external interrupt pins
- 16 analog input pins
- 19 PWM pins
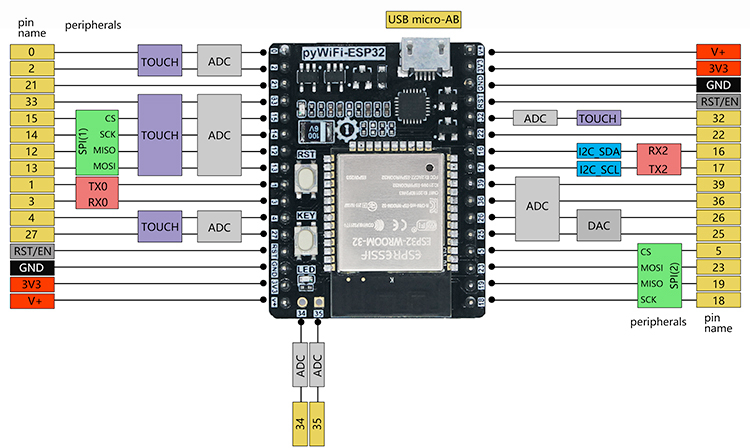
pyWiFi-ESP32 Development Board Kit Pinout
The pyWiFi-ESP32 pinout follows standard ESP32 GPIO layout with 30+ pins for extensive functionality. Power pins include 3V3 for 3.3V supply and GND for ground. Communication pins like TXD0 and RXD0 handle UART, while GPIO pins (0-39) support digital I/O, ADC, DAC, PWM, I2C, SPI, and more.
ADC channels provide 12-bit analog input, DAC offers analog output, and touch sensors enable capacitive touch interfaces. The board's flexible pinout makes it perfect for sensor integration and IoT prototyping.
✅ Safe Pins to Use
For general GPIO usage, these are the safest and most flexible choices:
Why Are These Pins Safe?
- Not involved in bootstrapping → No impact on device boot mode or system startup
- Not linked to flash memory or PSRAM → Won't interfere with storage or memory access
- Not dedicated to USB or JTAG → Free for general use without affecting debugging
- No special hardware connections → Freely assignable without internal conflicts
⚠️ Pins to Avoid or Use with Caution
Some pins are reserved for critical functions like bootstrapping, JTAG debugging, USB communication, and flash memory operations. Misusing these pins may lead to boot failures, programming issues, USB conflicts, or disruptions in flash storage.
Critical Pin Categories:
- 🛠️ Strapping Pins: Control boot behavior and flash voltage selection
- 🔗 JTAG Debugging Pins: Required for low-level debugging
- 🔌 USB Communication Pins: Used for USB Serial/JTAG communication
- ⚡ Flash Memory & SPI Pins: Connected to SPI flash memory and PSRAM
- 📡 UART Serial Communication Pins: Used for debugging and firmware uploads
| PIN | Label | Reason | Function |
|---|---|---|---|
| IO0 | GPIO0 | Must be HIGH during boot for normal startup; if held LOW on reset, forces flash programming mode. | 🛠️ Strapping |
| IO2 | GPIO2 | If driven HIGH on reset (while IO0 is LOW), selects an unsupported SDIO boot mode, causing boot failure. | 🛠️ Strapping |
| IO4 | GPIO4 | Sampled at reset for boot config; should not be driven at boot (affects boot mode timing). | 🛠️ Strapping |
| IO5 | GPIO5 | Must be HIGH during boot; if pulled LOW at reset, alters SDIO slave timing and may prevent normal boot. | 🛠️ Strapping |
| IO12 | MTDI (GPIO12) | Keep LOW during boot (internal PD); pulling HIGH at reset selects 1.8V flash mode, causing flash brownout if 3.3V flash is used. | 🛠️ Strapping |
pyWiFi-ESP32 Kit Contents
📦 Included Components
- pyWiFi-ESP32 Board: Main ESP32 development board
- pyBase: Expansion base board with additional interfaces
- 0.96" OLED Display: I2C OLED screen for output
- Micro USB Cable: For power and programming
- Sensors: Atmospheric Pressure, Water Level, Soil Humidity, Ultrasonic, Human Infrared, Photosensitive
🎯 Perfect For
This kit is ideal for learning MicroPython, IoT development, and building sensor-based projects. The included sensors enable quick prototyping of environmental monitoring, automation, and interactive applications.
💡 Getting Started
Connect via Micro USB, install MicroPython firmware using esptool, and start coding with Thonny IDE or similar. The kit provides everything needed for immediate IoT experimentation.
pyWiFi-ESP32 Development Board Kit Useful Links
pyWiFi-ESP32 Development Board Kit Pin Mappings
This development board provides 30 digital IO pins, out of which 16 can be used as external interrupt pins , 16 as analog input pins and 19 pins have Pulse-Width Modulation (PWM) .
| Pin | Function | ESP Pin | Input/Output | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4 | IO0 | GPIO0 | BIDIRECTIONAL | GPIO0, Boot Mode Selection, Button |
| 5 | IO2 | GPIO2 | BIDIRECTIONAL | GPIO2, General Purpose I/O, LED |
| 6 | IO4 | GPIO4 | BIDIRECTIONAL | GPIO4, General Purpose I/O |
| 7 | IO5 | GPIO5 | BIDIRECTIONAL | GPIO5, General Purpose I/O |
| 8 | IO12 | GPIO12 | BIDIRECTIONAL | GPIO12, ADC or GPIO |
| 9 | IO13 | GPIO13 | BIDIRECTIONAL | GPIO13, ADC or GPIO |
| 10 | IO14 | GPIO14 | BIDIRECTIONAL | GPIO14, ADC or GPIO |
| 11 | IO15 | GPIO15 | BIDIRECTIONAL | GPIO15, ADC or GPIO |
| 12 | IO16 | GPIO16 | BIDIRECTIONAL | GPIO16, General Purpose I/O |
| 13 | RX | GPIO3 | INPUT | UART0 Receive |
| 14 | TX | GPIO1 | OUTPUT | UART0 Transmit |
| 15 | IO17 | GPIO17 | BIDIRECTIONAL | GPIO17, General Purpose I/O |
| 16 | IO18 | GPIO18 | BIDIRECTIONAL | GPIO18, General Purpose I/O |
| 17 | IO19 | GPIO19 | BIDIRECTIONAL | GPIO19, General Purpose I/O |
| 18 | IO21 | GPIO21 | BIDIRECTIONAL | GPIO21, I2C SDA |
| 19 | IO22 | GPIO22 | BIDIRECTIONAL | GPIO22, I2C SCL |
| 20 | IO23 | GPIO23 | BIDIRECTIONAL | GPIO23, SPI MOSI |
| 21 | IO25 | GPIO25 | BIDIRECTIONAL | GPIO25, DAC1 |
| 22 | IO26 | GPIO26 | BIDIRECTIONAL | GPIO26, DAC2 |
| 23 | IO27 | GPIO27 | BIDIRECTIONAL | GPIO27, ADC |
| 24 | IO32 | GPIO32 | BIDIRECTIONAL | GPIO32, ADC |
| 25 | IO33 | GPIO33 | BIDIRECTIONAL | GPIO33, ADC |
| 26 | IO34 | GPIO34 | INPUT | GPIO34, ADC Input Only |
| 27 | IO35 | GPIO35 | INPUT | GPIO35, ADC Input Only |
pyWiFi-ESP32 Development Board Kit Pins Mapping Arduino IDE
Below you can find the pyWiFi-ESP32 Development Board Kit pinout. This development board provides 30 digital IO pins, out of which 16 can be used as external interrupt pins, 16 as analog input pins and 19 pins have Pulse-Width Modulation (PWM).
| Pin | Analog | Touch | PWM | Other |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | T1 | |||
| 1 | PWM | TX | ||
| 2 | A12 | T2 | PWM | |
| 3 | PWM | RX | ||
| 4 | A10 | T0 | PWM | |
| 5 | PWM | |||
| 12 | A15 | T5 | PWM | |
| 13 | A14 | T4 | PWM | |
| 14 | A16 | T6 | PWM | |
| 15 | A13 | T3 | PWM | |
| 16 | PWM | |||
| 17 | PWM | |||
| 18 | PWM | |||
| 19 | PWM | |||
| 21 | PWM | SDA | ||
| 22 | PWM | SCL | ||
| 23 | PWM | MOSI | ||
| 25 | A18 | DAC1 | ||
| 26 | A19 | DAC2 | ||
| 27 | A17 | T8 | PWM | |
| 32 | A4 | T9 | PWM | |
| 33 | A5 | T10 | PWM | |
| 34 | A6 | INPUT | ||
| 35 | A7 | INPUT |
Default Tools for pyWiFi-ESP32 Development Board Kit
| Bootloader tool | esptool_py |
| Uploader tool | esptool_py |
| Network uploader tool | esp_ota |
| Bootloader address | 0x1000 |
| Flash mode | dio |
| Boot mode | dio |
| Maximum upload size | 1280 Kb (1310720 B) |
| Maximum data size | 320 Kb (327680 B) |
The pyWiFi-ESP32 Development Board Kit development board by default uses esptool_py uploader tool, esp_ota network uploader tool for Over-the-air (OTA) uploads and esptool_py bootloader tool. The bootloader starts at address "0x1000". Flash mode and boot mode for pyWiFi-ESP32 Development Board Kit development board by default is dio and dio respectively.