ESP32-H2 Super Mini Development Board
Code name: ESP32H2_DEV
ESP32-H2 Super Mini development board is based on esp32h2 microcontroller and uses riscv32 architecture. This board has a maximum CPU frequency of 96 MHz and a flash size of 4MB.
About ESP32-H2 Super Mini
The ESP32-H2 SuperMini is an ultra-low-power IoT development board based on the Espressif ESP32-H2 chip. It features a 32-bit RISC-V single-core processor running at up to 96 MHz. The board integrates IEEE 802.15.4 support, making it compatible with Thread and Zigbee protocols for robust mesh networking. Additionally, it includes Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) and operates in the 2.4 GHz band with a data rate of up to 250 Kbps. The ESP32-H2 SuperMini is designed for applications requiring low-power consumption, RF stability, and secure wireless communication, making it ideal for IoT, smart home, and industrial automation.
🆚 Wondering how the ESP32-S3 SuperMini compares to other SuperMini boards? Check out our full comparison guide to see how it stacks up against the C3, C3 Plus, C6, and H2.
Where to Buy

Prices are subject to change. We earn from qualifying purchases as an Amazon Associate.
Technical Specifications
🛰️ Connectivity
🧠 Microcontroller
✨ Features
- RISC-V 32-bit single-core CPU running at up to 96 MHz
- 128 KB ROM, 320 KB SRAM, 4 KB Low-Power SRAM
- 4 MB in-package flash memory
- Supports IEEE 802.15.4 (Thread and Zigbee)
- Bluetooth 5 Low Energy (BLE) support
- Operates in the 2.4 GHz band with 250 Kbps data rate
- USB Type-C interface for easy programming
- Low-power consumption for battery-operated devices
- 11 digital IO pins
- 22 external interrupt pins
- 6 analog input pins
- 11 PWM pins
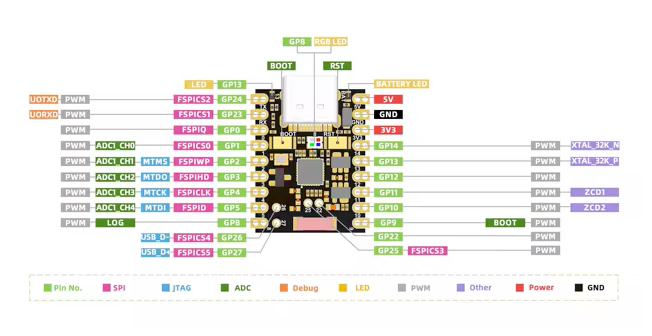
ESP32-H2 Super Mini Pinout
The ESP32-H2 Super Mini pinout is optimized for low-power and wireless communication applications. It includes essential power pins such as 5V, 3.3V, and GND for stable operation.
The board provides communication interfaces like RX and TX for UART, SDA and SCL for I2C, and MISO, MOSI, SCK, and SS for SPI, ensuring seamless integration with external devices.
For wireless connectivity, the ESP32-H2 SuperMini supports IEEE 802.15.4 for Thread/Zigbee and Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE), making it an excellent choice for mesh networking applications.
✅ Safe Pins to Use
For general GPIO usage, these are the safest and most flexible choices:
Why Are These Pins Safe?
- Not involved in bootstrapping → No impact on device boot mode or system startup
- Not linked to flash memory or PSRAM → Won't interfere with storage or memory access
- Not dedicated to USB or JTAG → Free for general use without affecting debugging
- No special hardware connections → Freely assignable without internal conflicts
⚠️ Pins to Avoid or Use with Caution
Some pins are reserved for critical functions like bootstrapping, JTAG debugging, USB communication, and flash memory operations. Misusing these pins may lead to boot failures, programming issues, USB conflicts, or disruptions in flash storage.
Critical Pin Categories:
- 🛠️ Strapping Pins: Control boot behavior and flash voltage selection
- 🔗 JTAG Debugging Pins: Required for low-level debugging
- 🔌 USB Communication Pins: Used for USB Serial/JTAG communication
- ⚡ Flash Memory & SPI Pins: Connected to SPI flash memory and PSRAM
- 📡 UART Serial Communication Pins: Used for debugging and firmware uploads
| PIN | Label | Reason | Function |
|---|---|---|---|
| IO0 | GPIO0 | Connected to the external (or in-package) flash memory as a data line; cannot be repurposed without interfering with program storage. | ⚡ Flash |
| IO1 | GPIO1 | Used to select the SPI flash chip (not brought out on modules with in-package flash); needed for flash access, so it should not be used as a general IO. | ⚡ Flash |
| IO2 | MTMS | Serves as the flash memory’s write-protect pin and the JTAG TMS line; using it as GPIO can disrupt flash operation or JTAG debugging. | ⚡ Flash |
| IO3 | MTDO | Serves as the flash HOLD (D3) line and the JTAG TDO output; repurposing it can interfere with flash reads/writes or JTAG debugging. | ⚡ Flash |
| IO4 | MTCK | Acts as the SPI flash clock line and the JTAG clock; cannot be used as GPIO without halting flash operation or debug capability. | ⚡ Flash |
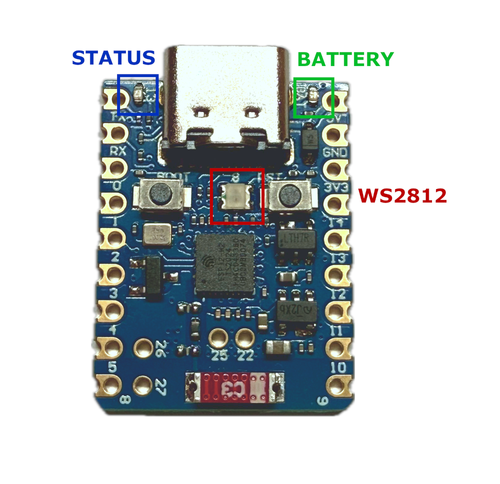
ESP32-H2 Super Mini On-Board LEDs
The ESP32-H2 Supermini features three onboard LEDs: a green battery indicator, a user-controllable blue LED, and a WS2812 RGB LED. Note that the Blue LED and WS2812 share GPIO13 and GPIO8 respectively, and may interfere if both are driven simultaneously due to signal timing constraints.
🟢 Green LED – Battery Charge Indicator
- GPIO:
None - Control: Not controllable via GPIO
- Behavior:
- ⚡ Charging → LED on
- ✅ Battery connected → LED off
- 🔋 No battery → LED blinks
🔵 Blue LED – User Controllable
- GPIO:
GPIO13 - Control:
digitalWrite(), ESPHome GPIO output
void setup() {
pinMode(13, OUTPUT);
}
void loop() {
digitalWrite(13, HIGH);
delay(1000);
digitalWrite(13, LOW);
delay(1000);
}
output:
- platform: gpio
pin: 13
id: blue_led
light:
- platform: binary
name: "Blue LED"
output: blue_led
🌈 WS2812 LED – Programmable RGB
- GPIO:
GPIO8 - Control: FastLED, NeoPixel, etc.
#include <FastLED.h>
#define NUM_LEDS 1
#define DATA_PIN 8
CRGB leds[NUM_LEDS];
void setup() {
FastLED.addLeds<NEOPIXEL, DATA_PIN>(leds, NUM_LEDS);
}
void loop() {
leds[0] = CRGB::Red; FastLED.show(); delay(1000);
leds[0] = CRGB::Green; FastLED.show(); delay(1000);
leds[0] = CRGB::Blue; FastLED.show(); delay(1000);
light:
- platform: neopixelbus
type: GRB
pin: 8
num_leds: 1
name: "Onboard RGB LED"ESP32-H2 Super Mini Pin Mappings
This development board provides 11 digital IO pins, out of which 22 can be used as external interrupt pins , 6 as analog input pins and 11 pins have Pulse-Width Modulation (PWM) .
| Pin | Function | ESP Pin | Input/Output | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 5V | 5V | power input | 5V power input for the board |
| 2 | GND | GND | power ground | Ground connection |
| 3 | 3V3 | 3.3V | power output | 3.3V power output for peripherals |
| 4 | IO0 | GP0 | bidirectional | GPIO |
| 5 | IO1 | GP1 | bidirectional | GPIO, ADC pin |
| 6 | IO2 | GP2 | bidirectional | GPIO, ADC pin |
| 7 | IO3 | GP3 | bidirectional | GPIO, ADC pin |
| 8 | IO4 | GP4 | bidirectional | GPIO, ADC pin |
| 9 | IO5 | GP5 | bidirectional | GPIO, ADC pin |
| 12 | IO8 | GP8 | bidirectional | GPIO, LOG |
| 13 | IO9 | GP9 | bidirectional | GPIO, BOOT |
| 14 | IO10 | GP10 | bidirectional | GPIO |
| 15 | IO11 | GP11 | bidirectional | GPIO |
| 16 | IO12 | GP12 | bidirectional | GPIO |
| 17 | IO13 | GP13 | bidirectional | GPIO, LED |
| 18 | IO14 | GP14 | bidirectional | GPIO |
| 19 | IO22 | GP2 | bidirectional | GPIO |
| 20 | IO23 | GP23 | bidirectional | GPIO |
| 22 | IO25 | GP25 | bidirectional | GPIO |
| 23 | IO26 | GP26 | bidirectional | GPIO |
| 24 | IO27 | GP27 | bidirectional | GPIO |
ESP32-H2 Super Mini Pins Mapping Arduino IDE
Below you can find the ESP32-H2 Super Mini pinout. This development board provides 11 digital IO pins, out of which 22 can be used as external interrupt pins, 6 as analog input pins and 11 pins have Pulse-Width Modulation (PWM).
| Pin | Analog | Touch | PWM | Other |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | A0 | |||
| 1 | A1 | |||
| 2 | A2 | |||
| 3 | A3 | |||
| 4 | A4 | SCK | ||
| 5 | A5 | MISO | ||
| 6 | MOSI | |||
| 7 | SS | |||
| 8 | SDA | |||
| 9 | SCL | |||
| 20 | RX | |||
| 21 | TX |
Default Tools
| Bootloader tool | esptool_py |
| Uploader tool | esptool_py |
| Network uploader tool | esp_ota |
| Bootloader address | 0x0 |
| Flash mode | qio |
| Boot mode | qio |
| Maximum upload size | 1024 Kb (1048576 B) |
| Maximum data size | 256 Kb (262144 B) |
The ESP32-H2 Super Mini development board by default uses esptool_py uploader tool, esp_ota network uploader tool for Over-the-air (OTA) uploads and esptool_py bootloader tool. The bootloader starts at address "0x0". Flash mode and boot mode for ESP32-H2 Super Mini development board by default is qio and qio respectively.