JSN-SR04T Waterproof Ultrasonic Distance Sensor
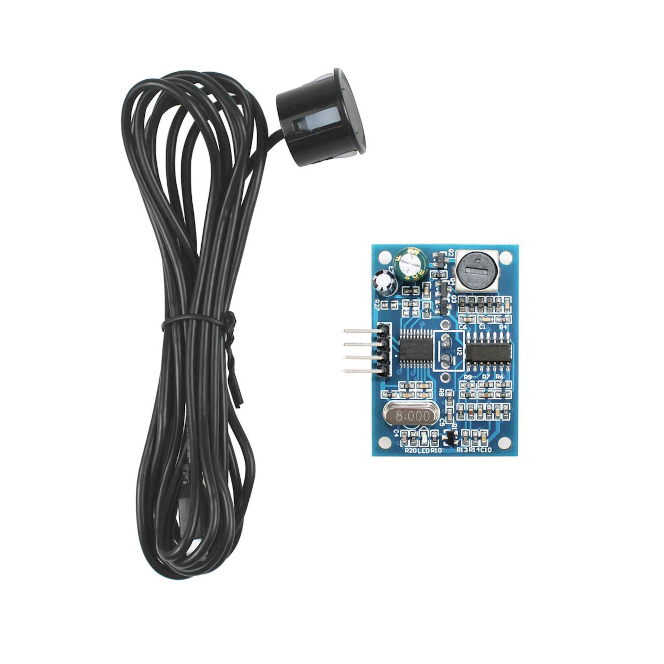

View on Amazon
Overview
About JSN-SR04T Waterproof Ultrasonic Distance Sensor
The JSN-SR04T is a waterproof ultrasonic sensor designed for long-range distance measurement in outdoor and industrial environments. With a measurement range of 25 cm to 600 cm, it is ideal for liquid level sensing, parking sensors, and proximity detection.
⚡ Key Features
- Extended Measurement Range – Detects distances from 25 cm to 600 cm.
- Waterproof & Dustproof Design – Ideal for harsh outdoor conditions.
- Trigger & Echo Mechanism – Operates similarly to the HC-SR04 for easy integration.
- ESP32 & Arduino Compatible – Works seamlessly with microcontrollers for automation projects.
With its rugged build and reliable performance, the JSN-SR04T is perfect for applications requiring water-resistant distance sensing. 🚀
Get Your JSN-SR04T



💡 Prices are subject to change. We earn from qualifying purchases as an Amazon Associate.
JSN-SR04T Specifications
Complete technical specification details for JSN-SR04T Waterproof Ultrasonic Distance Sensor
📊 Technical Parameters
JSN-SR04T Pinout
The JSN-SR04T has 4 pins using the trigger/echo mechanism for ultrasonic distance measurement.
Visual Pinout Diagram
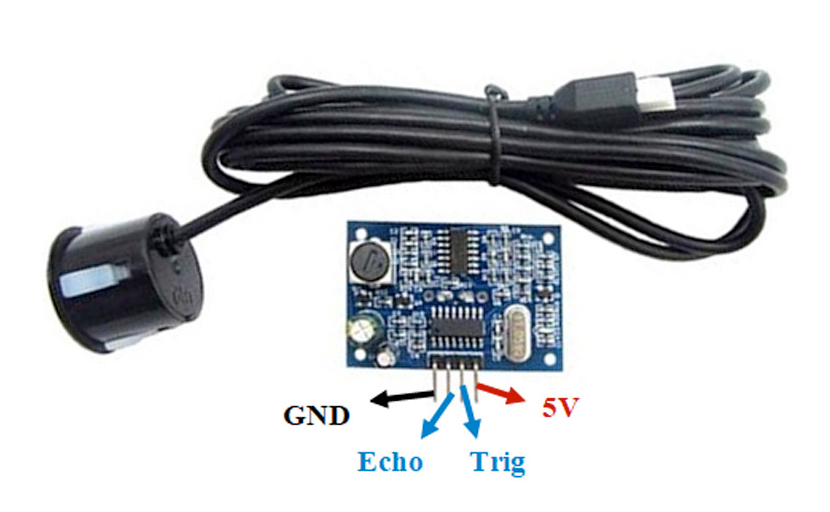
Pin Types
Quick Tips
Object],[object Object]
Object],Waterproof design (IP67 rated probe)
Object],[object Object]
Pin Descriptions
| Pin Name | Type | Description | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
1 VCC | Power | Power supply input (5V). Requires stable 5V power. | Use regulated 5V supply for accurate measurements. |
2 GND | Power | Ground connection. Connect to system ground. | |
3 Trigger (TRIG) | Input | Trigger input. Send 10µs HIGH pulse to initiate measurement. | Connect to GPIO output pin. |
4 Echo | Output | Echo output. Pulse width represents distance (58µs per cm). | Connect to GPIO input. Use voltage divider for 3.3V systems. |
Wiring JSN-SR04T to ESP32
To interface the JSN-SR04T with an ESP32, connect VCC to 5V, GND to ground, Trigger to GPIO 5, and Echo to GPIO 18 (through voltage divider for 3.3V protection).
Visual Wiring Diagram
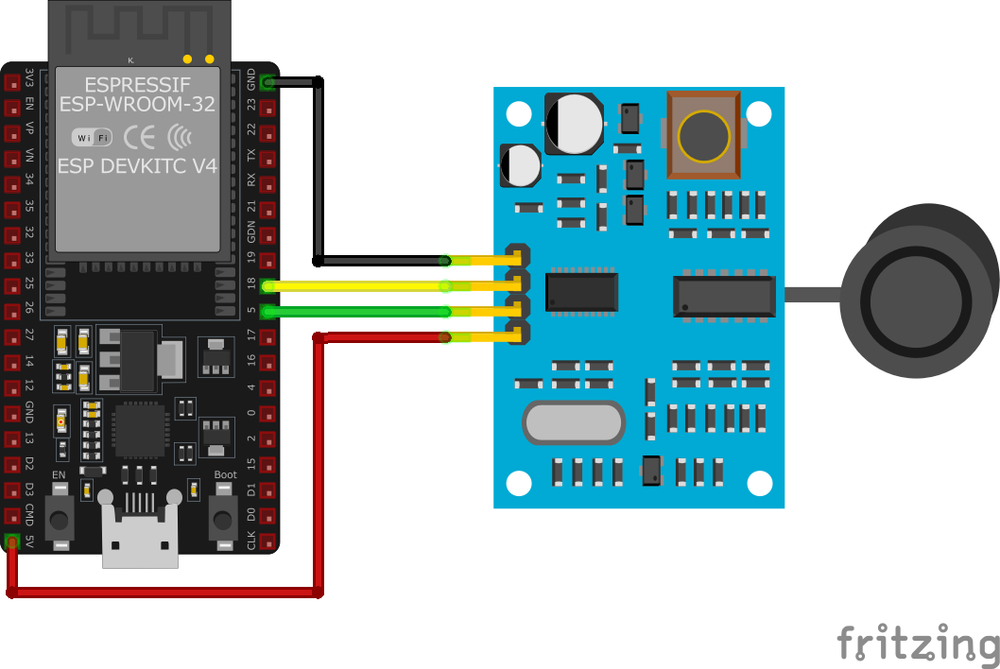
Connection Status
Protocol
Pin Connections
| JSN-SR04T Pin | Connection | ESP32 Pin | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
1 VCC Required | 5V | Power supply (5V). Use stable regulated power. | |
2 GND Required | GND | Ground connection. | |
3 Trigger Required | GPIO 5 | Trigger input. Send 10µs HIGH pulse to start measurement. | |
4 Echo Required | GPIO 18 | Echo output. Use voltage divider (1kΩ + 2kΩ) for 3.3V protection. |
Object]
Object]
Object]
Object]
Object]
Object]
Object]
NewPing or Ultrasonic library for Arduino/ESP32
Object]
Object]
JSN-SR04T Troubleshooting
Common issues and solutions to help you get your sensor working
Common Issues
Issue: The JSN-SR04T sensor provides constant or incorrect distance measurements, regardless of the actual distance to the target.
Possible causes include incorrect wiring, insufficient power supply, or improper sensor configuration.
Solution: Ensure that the sensor is connected to a stable 5V power source, as it requires 5V for proper operation. Verify that the TRIG and ECHO pins are correctly connected to the appropriate GPIO pins on the microcontroller. Confirm that the sensor is properly initialized in your code, and that the trigger pulse duration is set correctly; some users have found that a 15-microsecond trigger pulse can improve reliability.
Issue: The sensor outputs distance readings that vary significantly, even when the target distance remains constant.
Possible causes include environmental factors such as temperature variations, soft or angled target surfaces, or electrical noise.
Solution: Position the sensor perpendicular to a hard, flat target surface to ensure accurate reflections. Be aware that temperature changes can affect the speed of sound; consider implementing temperature compensation if precise measurements are required. Implement averaging of multiple readings in your code to mitigate occasional erroneous data.
Issue: The microcontroller fails to detect the JSN-SR04T sensor, or the sensor does not respond to trigger signals.
Possible causes include incorrect pin assignments in the code, lack of proper initialization, or defective sensor module.
Solution: Double-check the pin assignments in your code to ensure they match the physical connections. Confirm that the sensor is properly initialized in the setup section of your code. If the issue persists, test the sensor with a known working setup or replace it to rule out hardware failure.
Issue: External factors cause the sensor to produce unreliable readings.
Possible causes include high ambient noise levels, temperature variations, or obstacles in the sensor's field of view.
Solution: Operate the sensor in a controlled environment to minimize acoustic and electrical noise. Ensure that there are no unintended obstacles within the sensor's detection range that could cause false readings.
Debugging Tips
Use the Serial Monitor to check for error messages and verify the sensor's output. Add debug prints in your code to track the sensor's state.
Use a multimeter to verify voltage levels and check for continuity in your connections. Ensure the power supply is stable and within the sensor's requirements.
Additional Resources
JSN-SR04T Programming Examples
Ready-to-use code examples for different platforms and frameworks
#define TRIG_PIN 5
#define ECHO_PIN 18
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
pinMode(TRIG_PIN, OUTPUT);
pinMode(ECHO_PIN, INPUT);
Serial.println("JSN-SR04T Distance Sensor Example");
}
void loop() {
long duration;
float distance;
// Trigger the sensor
digitalWrite(TRIG_PIN, LOW);
delayMicroseconds(2);
digitalWrite(TRIG_PIN, HIGH);
delayMicroseconds(10);
digitalWrite(TRIG_PIN, LOW);
// Read the Echo pin
duration = pulseIn(ECHO_PIN, HIGH);
// Calculate distance in cm
distance = duration * 0.034 / 2;
Serial.print("Distance: ");
Serial.print(distance);
Serial.println(" cm");
delay(500);
}TRIG_PIN and ECHO_PIN are defined to connect the sensor to GPIO pins 9 and 10, respectively. The setup() function initializes these pins and configures the Serial Monitor. In the loop(), a 10 µs pulse is sent to the Trigger pin to start measurement, and the duration of the Echo pin's HIGH state is measured using the pulseIn() function. The distance is calculated using the formula duration * 0.034 / 2, which converts the time into distance in centimeters.#include <stdio.h>
#include "freertos/FreeRTOS.h"
#include "freertos/task.h"
#include "driver/gpio.h"
#include "esp_timer.h"
#define TRIG_PIN GPIO_NUM_5
#define ECHO_PIN GPIO_NUM_18
void app_main() {
gpio_set_direction(TRIG_PIN, GPIO_MODE_OUTPUT);
gpio_set_direction(ECHO_PIN, GPIO_MODE_INPUT);
while (1) {
// Send trigger pulse
gpio_set_level(TRIG_PIN, 0);
ets_delay_us(2);
gpio_set_level(TRIG_PIN, 1);
ets_delay_us(10);
gpio_set_level(TRIG_PIN, 0);
// Measure echo pulse width
uint64_t start_time = esp_timer_get_time();
while (!gpio_get_level(ECHO_PIN)); // Wait for HIGH
uint64_t echo_start = esp_timer_get_time();
while (gpio_get_level(ECHO_PIN)); // Wait for LOW
uint64_t echo_end = esp_timer_get_time();
uint64_t duration = echo_end - echo_start;
float distance = (duration * 0.034) / 2;
printf("Distance: %.2f cm\n", distance);
vTaskDelay(pdMS_TO_TICKS(500));
}
}gpio_set_level() function sends a 10 µs pulse to the Trigger pin. The time taken for the Echo pin to go HIGH and then LOW is measured using esp_timer_get_time(), which provides timestamps in microseconds. The distance is calculated based on the formula (duration * 0.034) / 2. The program continuously measures and prints the distance in centimeters every 500 ms.sensor:
- platform: ultrasonic
trigger_pin: GPIO5
echo_pin: GPIO18
name: "JSN-SR04T Distance"
update_interval: 500ms
accuracy_decimals: 1
timeout: 2.0multrasonic platform to interface with the JSN-SR04T sensor. The trigger_pin and echo_pin specify the GPIO pins connected to the sensor. The name assigns a user-friendly identifier ('JSN-SR04T Distance') for use in platforms like Home Assistant. The update_interval of 500 ms specifies how often distance measurements are taken, while accuracy_decimals ensures measurements are displayed to one decimal place. The timeout prevents errors in case of no response within the specified time.platformio.ini
[env:esp32dev]
platform = espressif32
board = esp32dev
framework = arduino
monitor_speed = 115200main.cpp
#define TRIG_PIN 5
#define ECHO_PIN 18
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
pinMode(TRIG_PIN, OUTPUT);
pinMode(ECHO_PIN, INPUT);
}
void loop() {
long duration;
float distance;
// Trigger the sensor
digitalWrite(TRIG_PIN, LOW);
delayMicroseconds(2);
digitalWrite(TRIG_PIN, HIGH);
delayMicroseconds(10);
digitalWrite(TRIG_PIN, LOW);
// Read the Echo pin
duration = pulseIn(ECHO_PIN, HIGH);
// Calculate distance
distance = duration * 0.034 / 2;
Serial.print("Distance: ");
Serial.print(distance);
Serial.println(" cm");
delay(500);
}TRIG_PIN and ECHO_PIN for sensor operation. A short 10 µs pulse triggers the measurement, and the pulse duration is read on the Echo pin using the pulseIn() function. The calculated distance is printed to the Serial Monitor every 500 ms.from machine import Pin, time_pulse_us
from time import sleep
# Define pins for Trigger and Echo
TRIG_PIN = 5
ECHO_PIN = 18
# Initialize Trigger and Echo pins
trig = Pin(TRIG_PIN, Pin.OUT)
echo = Pin(ECHO_PIN, Pin.IN)
def measure_distance():
# Send a 10 µs pulse to the Trigger pin
trig.low()
sleep(0.000002) # 2 µs
trig.high()
sleep(0.00001) # 10 µs
trig.low()
# Measure the duration of the Echo pulse
duration = time_pulse_us(echo, 1, 30000) # Timeout after 30 ms (no response)
# Calculate distance in cm (speed of sound = 343 m/s)
distance = (duration * 0.0343) / 2
return distance
print("JSN-SR04T Distance Sensor Example")
while True:
distance = measure_distance()
if distance > 0:
print("Distance: {:.2f} cm".format(distance))
else:
print("Out of range or no object detected.")
sleep(0.5)time_pulse_us() function measures the duration of the Echo pulse in microseconds, with a timeout of 30 ms to prevent infinite waiting. The distance is calculated using the formula (duration * 0.0343) / 2, where 0.0343 cm/µs is the speed of sound. The script continuously measures and prints the distance to the console every 500 ms. If no response is detected, it prints an 'Out of range' message.Wrapping Up JSN-SR04T
The ESP32 JSN-SR04T Waterproof Ultrasonic Distance Sensor is a powerful distance sensor that offers excellent performance and reliability. With support for multiple development platforms including Arduino, ESP-IDF, ESPHome, PlatformIO, and MicroPython, it's a versatile choice for your IoT projects.
Best Practices
For optimal performance, ensure proper wiring and follow the recommended configuration for your chosen development platform.
Safety First
Always verify power supply requirements and pin connections before powering up your project to avoid potential damage.
Ready to Start Building?
Now that you have all the information you need, it's time to integrate the JSN-SR04T into your ESP32 project and bring your ideas to life!
Explore Alternative Sensors
Looking for alternatives to the JSN-SR04T? Check out these similar sensors that might fit your project needs.

VL53L1X Time-of-Flight Sensor
The VL53L1X is a high-accuracy long-distance laser-ranging sensor from STMicroelectronics. It uses a 940nm VCSEL emitter and advanced SPAD...

VL6180X Time-of-Flight Sensor
The VL6180X is a short-range proximity and ambient light sensor that combines a 3-in-1 system: IR emitter, sensor, and ranging processor. It...

A02YYUW Waterproof Ultrasonic Distance Sensor
The A02YYUW is a waterproof ultrasonic distance sensor ideal for outdoor and industrial applications. With a measuring range of up to 4.5...





