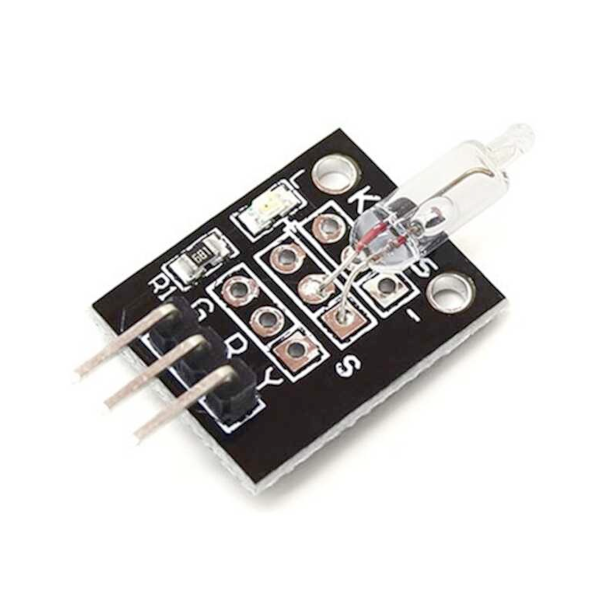
KY-017 Mercury Tilt Switch Module

View on Amazon
Overview
About KY-017 Mercury Tilt Switch Module
The KY-017 Mercury Tilt Switch Module is a sensor that detects tilt or inclination. It contains a mercury switch that closes the circuit when tilted to a certain angle, allowing current to flow. This module operates at a voltage range of 3.3V to 5.5V and provides a digital output signal. It’s commonly used in applications such as tilt detection, motion sensing, and orientation monitoring.
Get Your KY-017



💡 Prices are subject to change. We earn from qualifying purchases as an Amazon Associate.
KY-017 Specifications
Complete technical specification details for KY-017 Mercury Tilt Switch Module
📊 Technical Parameters
KY-017 Pinout
The **KY-017** is a 3-pin mercury tilt switch sensor module:
Visual Pinout Diagram
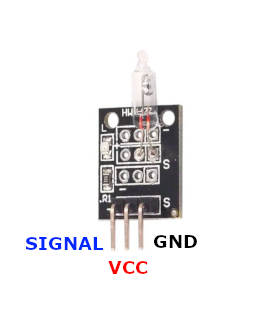
Pin Types
Quick Tips
**Interface**: Digital output (tilt/orientation detection),⚠️ **Sensor**: Mercury switch (handle with care - contains mercury)
**Detection**: Circuit closes when tilted beyond threshold angle,⚡ **Power**: 3.3V to 5.5V operation
**Operation**: Simple binary tilt detection (on/off),🎯 **Applications**: Tilt detection, orientation sensing, motion alarms, anti-theft
Pin Descriptions
| Pin Name | Type | Description | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
1 Pin (-) | Power | Ground connection | |
2 Pin (middle) | Power | Power supply | 3.3V to 5.5V |
3 Pin (S) | Communication | Digital signal output | Changes state when tilted |
Wiring KY-017 to ESP32
To interface the **KY-017** with an **ESP32** for tilt detection:
Visual Wiring Diagram
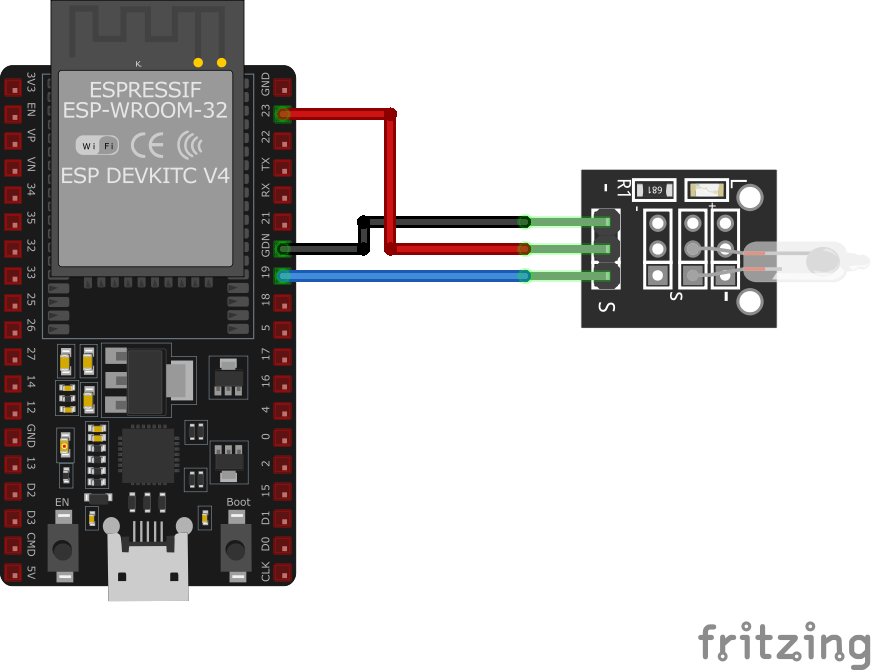
Connection Status
Protocol
Pin Connections
| KY-017 Pin | Connection | ESP32 Pin | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
1 Pin (-) Required | GND | Ground | |
2 Pin (middle) Required | 3.3V or 5V | Power supply | |
3 Pin (S) Required | GPIO4 | Digital input (any GPIO) |
**GPIO Selection**: Any digital GPIO pin works, GPIO4 is just an example
**Voltage**: Use 3.3V for ESP32 compatibility
**Safety**: Mercury switch - handle carefully, avoid breaking
**Binary Output**: Simple HIGH/LOW state based on tilt angle
KY-017 Troubleshooting
Common issues and solutions to help you get your sensor working
Common Issues
Issue: The sensor does not output any signal when tilted.
Solutions:
- Verify that all connections are secure and correctly placed.
- Ensure the module is receiving the appropriate voltage (3.3V to 5V).
- Check if the microcontroller's GPIO pin is correctly configured as an input.
Issue: The sensor outputs a signal without being tilted.
Solutions:
- Ensure the module is mounted securely to prevent unintended movement.
- Check for external vibrations or movements that might affect the sensor.
- Implement software debouncing to filter out spurious signals.
Debugging Tips
Use the Serial Monitor to check for error messages and verify the sensor's output. Add debug prints in your code to track the sensor's state.
Use a multimeter to verify voltage levels and check for continuity in your connections. Ensure the power supply is stable and within the sensor's requirements.
Additional Resources
KY-017 Programming Examples
Ready-to-use code examples for different platforms and frameworks
int tiltPin = 10; // Tilt sensor connected to digital pin 10
int ledPin = 13; // LED connected to digital pin 13
int sensorValue = 0;
void setup() {
pinMode(tiltPin, INPUT);
pinMode(ledPin, OUTPUT);
Serial.begin(9600);
Serial.println("KY-017 Tilt Sensor Test");
}
void loop() {
sensorValue = digitalRead(tiltPin);
if (sensorValue == LOW) {
digitalWrite(ledPin, HIGH);
Serial.println("Tilt detected");
} else {
digitalWrite(ledPin, LOW);
}
delay(1000);
}This Arduino code sets up the KY-017 tilt sensor on digital pin 10 and an LED on digital pin 13. When the sensor detects a tilt (sensor output is LOW), the LED lights up, and a message is printed to the serial monitor. The status is checked every second.
#include <stdio.h>
#include "freertos/FreeRTOS.h"
#include "freertos/task.h"
#include "driver/gpio.h"
#define TILT_SENSOR_PIN GPIO_NUM_4
#define LED_PIN GPIO_NUM_2
void app_main(void) {
gpio_config_t io_conf = {
.pin_bit_mask = (1ULL << TILT_SENSOR_PIN) | (1ULL << LED_PIN),
.mode = GPIO_MODE_INPUT_OUTPUT,
.pull_up_en = GPIO_PULLUP_ENABLE,
.pull_down_en = GPIO_PULLDOWN_DISABLE,
.intr_type = GPIO_INTR_DISABLE
};
gpio_config(&io_conf);
printf("KY-017 Tilt Sensor Test\n");
while (1) {
int sensor_value = gpio_get_level(TILT_SENSOR_PIN);
if (sensor_value == 0) {
gpio_set_level(LED_PIN, 1);
printf("Tilt detected\n");
} else {
gpio_set_level(LED_PIN, 0);
}
vTaskDelay(pdMS_TO_TICKS(1000));
}
}This ESP-IDF code configures GPIO4 as an input for the KY-017 tilt sensor and GPIO2 as an output for an LED. When the sensor detects a tilt (sensor output is LOW), the LED turns on, and a message is printed to the console. The status is checked every second.
binary_sensor:
- platform: gpio
pin:
number: GPIO4
mode: INPUT_PULLUP
name: "KY-017 Tilt Sensor"
filters:
- delayed_on: 50ms
- delayed_off: 50ms
on_press:
- then:
- lambda: |-
ESP_LOGD("sensor", "Tilt detected!");This ESPHome configuration sets up the KY-017 mercury tilt switch as a binary sensor on GPIO4. The internal pull-up resistor is enabled, and debounce filtering is applied to prevent false triggering. When the sensor detects a tilt, a log message is generated.
platformio.ini
[env:esp32]
platform = espressif32
board = esp32dev
framework = arduinomain.cpp
#include <Arduino.h>
#define TILT_SENSOR_PIN 4
#define LED_PIN 2
void setup() {
pinMode(TILT_SENSOR_PIN, INPUT_PULLUP);
pinMode(LED_PIN, OUTPUT);
Serial.begin(115200);
Serial.println("KY-017 Tilt Sensor Test");
}
void loop() {
if (digitalRead(TILT_SENSOR_PIN) == LOW) {
Serial.println("Tilt detected");
digitalWrite(LED_PIN, HIGH);
} else {
digitalWrite(LED_PIN, LOW);
}
delay(1000);
}This PlatformIO code configures GPIO4 as an input with an internal pull-up resistor for the KY-017 tilt sensor. GPIO2 is used to control an LED. When the sensor detects a tilt (output is LOW), the LED turns on, and a message is printed to the serial monitor.
import machine
import time
TILT_SENSOR_PIN = machine.Pin(4, machine.Pin.IN, machine.Pin.PULL_UP)
LED_PIN = machine.Pin(2, machine.Pin.OUT)
while True:
if TILT_SENSOR_PIN.value() == 0:
print("Tilt detected")
LED_PIN.on()
else:
LED_PIN.off()
time.sleep(1)This MicroPython script configures GPIO4 as an input with a pull-up resistor for the KY-017 tilt sensor. GPIO2 controls an LED. When a tilt is detected (sensor output is LOW), the LED turns on, and a message is printed to the console.
Wrapping Up KY-017
The ESP32 KY-017 Mercury Tilt Switch Module is a powerful KY-0xx module sensor that offers excellent performance and reliability. With support for multiple development platforms including Arduino, ESP-IDF, ESPHome, PlatformIO, and MicroPython, it's a versatile choice for your IoT projects.
Best Practices
For optimal performance, ensure proper wiring and follow the recommended configuration for your chosen development platform.
Safety First
Always verify power supply requirements and pin connections before powering up your project to avoid potential damage.
Ready to Start Building?
Now that you have all the information you need, it's time to integrate the KY-017 into your ESP32 project and bring your ideas to life!
Explore Alternative Sensors
Looking for alternatives to the KY-017? Check out these similar sensors that might fit your project needs.
KY-025 Reed Switch Module
The KY-025 is a reed switch module that provides both analog and digital outputs. It is equipped with a potentiometer to adjust sensitivity...

KY-026 Flame Sensor Module
The KY-026 is a flame sensor module capable of detecting light in the 760 nm to 1100 nm wavelength range. It offers both analog and digital...

KY-020 Tilt Switch Module
The KY-020 is a tilt switch module that detects changes in orientation. It provides a digital signal output, making it suitable for...





