CCS811 Digital Gas Sensor
View on Amazon
Overview
About CCS811 Digital Gas Sensor
The CCS811 is an ultra-low power digital gas sensor designed for indoor air quality monitoring. It detects volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and provides equivalent CO₂ (eCO₂) levels, making it useful for smart home automation, HVAC systems, and environmental monitoring.
⚡ Key Features
- VOC & eCO₂ Detection – Monitors air quality and pollution levels.
- Integrated MCU & ADC – Simplifies processing and reduces external component requirements.
- Ultra-Low Power Consumption – Ideal for battery-powered applications.
- I²C Interface – Seamlessly integrates with ESP32, Arduino, and other microcontrollers.
Get Your CCS811



💡 Prices are subject to change. We earn from qualifying purchases as an Amazon Associate.
CCS811 Specifications
Complete technical specification details for CCS811 Digital Gas Sensor
📊 Technical Parameters
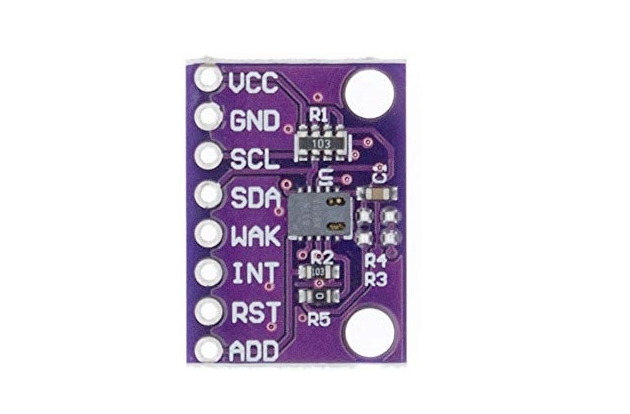
CCS811 Pinout
The CCS811 has 8 pins for I²C communication, power, and optional control signals.
Visual Pinout Diagram

Pin Types
Quick Tips
Object],Measures TVOC (0-1187 ppb) and eCO₂ (400-8192 ppm)
Object],Integrated MCU and ADC for simplified processing
20-minute burn-in period for first use,[object Object]
Pin Descriptions
| Pin Name | Type | Description | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
1 VDD | Power | Supply voltage (3.3V to 5V). Powers the sensor. | Use stable power supply for accurate readings. |
2 GND | Power | Ground connection. Connect to system ground. | |
3 SDA | I2C | I²C data line. Bidirectional data communication. | Connect to ESP32 GPIO 21. Requires pull-up resistor. |
4 SCL | I2C | I²C clock line. Clock signal for I²C communication. | Connect to ESP32 GPIO 22. Requires pull-up resistor. |
5 nWAKE | Control | Wake pin (active low). Pull low to enable communication. | Connect to GND for continuous operation, or GPIO for power saving. |
6 nINT | Interrupt | Interrupt pin (optional). Indicates data ready. | Active low. Connect to GPIO for interrupt-driven reading. |
7 nRESET | Control | Reset pin (active low). Used to reset the sensor. | Optional - pull high or connect to GPIO for software reset. |
8 ADDR | Address | I²C address select. Connect to GND (0x5A) or VDD (0x5B). | Default: GND (address 0x5A). |
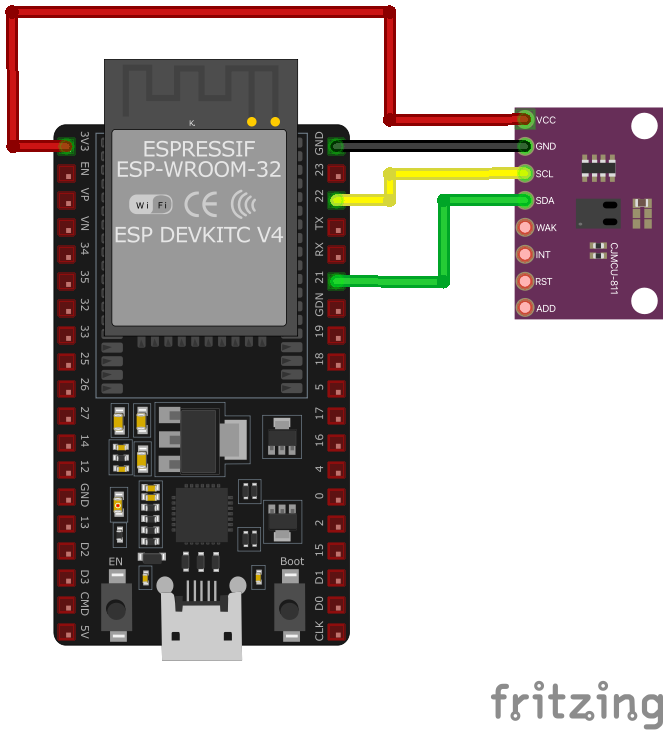
Wiring CCS811 to ESP32
To interface the CCS811 with an ESP32 via I²C, connect VDD to 3.3V or 5V, GND to ground, SDA to GPIO 21, SCL to GPIO 22, and nWAKE to GND.
Visual Wiring Diagram
Connection Status
Protocol
Pin Connections
| CCS811 Pin | Connection | ESP32 Pin | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
1 VDD Required | 3.3V | Power supply. Use 3.3V for most modules. | |
2 GND Required | GND | Ground connection. | |
3 SDA Required | GPIO 21 | I²C data line. Add 4.7kΩ pull-up resistor. | |
4 SCL Required | GPIO 22 | I²C clock line. Add 4.7kΩ pull-up resistor. | |
5 nWAKE Required | GND | Wake control. Connect to GND for continuous operation. | |
6 ADDR Required | GND or VDD | Address select. GND=0x5A (default), VDD=0x5B. | |
7 nINT Optional | Optional GPIO | Interrupt output for data ready indication. | |
8 nRESET Optional | Optional GPIO or VDD | Reset control. Pull high for normal operation. |
pull-up resistors (4.7kΩ) required on SDA and SCL
Object]
Object]
Object]
Object]
Adafruit_CCS811 or SparkFun_CCS811 library
Object]
use only - not for safety-critical gas detection
CCS811 Troubleshooting
Common issues and solutions to help you get your sensor working
Common Issues
Issue: The CCS811 sensor intermittently hangs when connected to an ESP8266, resulting in failed read attempts and the error: False (255).
Possible causes include the ESP8266's inability to handle the CCS811's clock stretching requirements, leading to communication failures.
Solution: Implement clock stretching support by adjusting the I2C communication settings. Adding a delay in the I2C operations can help accommodate the sensor's timing requirements. Additionally, ensure that the sensor's firmware is up to date and consider using a microcontroller with better I2C clock stretching support if the issue persists. ([forums.adafruit.com](https://forums.adafruit.com/viewtopic.php?t=121816))
Issue: The CCS811 sensor fails to initialize on an ESP8266, displaying errors such as: setup: CCS811 begin FAILED and CCS811: I2C error.
Possible causes include incorrect wiring, lack of pull-up resistors on the I2C lines, or the ESP8266's inadequate handling of I2C clock stretching.
Solution: Verify that SDA and SCL are correctly connected to the ESP8266's designated pins and that appropriate pull-up resistors (typically 4.7kΩ) are present on the I2C lines. Since the ESP8266 may not handle I2C clock stretching well, consider adding delays in the I2C communication or using a library that accounts for this limitation. Additionally, ensure that the sensor's WAKE pin is properly managed, either by connecting it to ground or controlling it via a GPIO pin. ([forum.arduino.cc](https://forum.arduino.cc/t/esp8266-ccs811-i2c-error/968846))
Issue: When interfacing the CCS811 sensor with a ESP32, the following error occurs: OSError: [Errno 121] Remote I/O error.
Possible causes include incorrect I2C address configuration, insufficient handling of clock stretching, or wiring issues.
Solution: Confirm the sensor's I2C address using i2cdetect and ensure your code references the correct address (commonly 0x5A or 0x5B). The Raspberry Pi may struggle with the CCS811's clock stretching; therefore, reduce the I2C bus speed by adding dtparam=i2c_arm_baudrate=10000 to /boot/config.txt and rebooting. Verify that the sensor's connections are secure and that the Raspberry Pi's I2C interface is enabled and functioning correctly. ([forum.sparkfun.com](https://forum.sparkfun.com/viewtopic.php?t=59017))
Issue: When reading data from the CCS811 sensor on Particle devices, the sensor returns an error code: ERROR! 2.
Possible causes include insufficient warm-up time for the sensor or issues with the initialization sequence.
Solution: Allow the sensor adequate warm-up time before attempting to read data, as the CCS811 requires a stabilization period after power-up. Ensure that your initialization code follows the recommended sequence as per the sensor's datasheet. If the problem persists, consider using an alternative library that may better handle the sensor's initialization and data retrieval processes. ([community.particle.io](https://community.particle.io/t/ccs811-reading-error-2/49491))
Debugging Tips
Use the Serial Monitor to check for error messages and verify the sensor's output. Add debug prints in your code to track the sensor's state.
Use a multimeter to verify voltage levels and check for continuity in your connections. Ensure the power supply is stable and within the sensor's requirements.
Additional Resources
CCS811 Programming Examples
Ready-to-use code examples for different platforms and frameworks
#include <Wire.h>
#include "Adafruit_CCS811.h"
Adafruit_CCS811 ccs;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
Wire.begin();
if (!ccs.begin()) {
Serial.println("Failed to start sensor! Please check your wiring.");
while (1);
}
// Wait for the sensor to be ready
while (!ccs.available());
}
void loop() {
if (ccs.available()) {
if (!ccs.readData()) {
Serial.print("eCO2: ");
Serial.print(ccs.geteCO2());
Serial.print(" ppm, TVOC: ");
Serial.print(ccs.getTVOC());
Serial.println(" ppb");
} else {
Serial.println("Error reading sensor data");
}
}
delay(1000);
}setup() function, the sensor is initialized, and the code waits until the sensor is ready. The loop() function checks if new data is available and reads the eCO₂ and TVOC levels, printing them to the Serial Monitor every second.#include <stdio.h>
#include "driver/i2c.h"
#include "ccs811.h"
#define I2C_MASTER_SCL_IO 22
#define I2C_MASTER_SDA_IO 21
#define I2C_MASTER_NUM I2C_NUM_0
#define I2C_MASTER_FREQ_HZ 100000
void app_main(void) {
i2c_config_t i2c_config = {
.mode = I2C_MODE_MASTER,
.sda_io_num = I2C_MASTER_SDA_IO,
.scl_io_num = I2C_MASTER_SCL_IO,
.sda_pullup_en = GPIO_PULLUP_ENABLE,
.scl_pullup_en = GPIO_PULLUP_ENABLE,
.master.clk_speed = I2C_MASTER_FREQ_HZ
};
i2c_param_config(I2C_MASTER_NUM, &i2c_config);
i2c_driver_install(I2C_MASTER_NUM, I2C_MODE_MASTER, 0, 0, 0);
ccs811_t sensor;
ccs811_init(&sensor, I2C_MASTER_NUM, CCS811_ADDR_LOW);
printf("Initializing CCS811\n");
if (ccs811_start(&sensor) != CCS811_OK) {
printf("Failed to start CCS811 sensor\n");
return;
}
while (1) {
uint16_t eco2, tvoc;
if (ccs811_read_data(&sensor, &eco2, &tvoc) == CCS811_OK) {
printf("eCO2: %d ppm, TVOC: %d ppb\n", eco2, tvoc);
} else {
printf("Error reading data from CCS811\n");
}
vTaskDelay(pdMS_TO_TICKS(1000));
}
}i2c:
sda: GPIO21
scl: GPIO22
sensor:
- platform: ccs811
eco2:
name: "eCO2"
tvoc:
name: "TVOC"
address: 0x5A
update_interval: 1ssensor platform fetches eCO₂ and TVOC data at 1-second intervals, displaying them as named sensors ('eCO2' and 'TVOC'). The I²C address is set to 0x5A, the default address for the CCS811.platformio.ini
[env:esp32dev]
platform = espressif32
board = esp32dev
framework = arduino
monitor_speed = 115200main.cpp
#include <Wire.h>
#include "Adafruit_CCS811.h"
Adafruit_CCS811 ccs;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
Wire.begin(21, 22); // SDA: GPIO21, SCL: GPIO22
if (!ccs.begin()) {
Serial.println("Failed to start sensor! Please check your wiring.");
while (1);
}
while (!ccs.available()); // Wait for the sensor to be ready
}
void loop() {
if (ccs.available()) {
if (!ccs.readData()) {
Serial.print("eCO2: ");
Serial.print(ccs.geteCO2());
Serial.print(" ppm, TVOC: ");
Serial.print(ccs.getTVOC());
Serial.println(" ppb");
} else {
Serial.println("Error reading sensor data");
}
}
delay(1000);
}from machine import I2C, Pin
import time
# CCS811 I2C address
CCS811_ADDR = 0x5A
# Register addresses
MEAS_MODE = 0x01
ALG_RESULT_DATA = 0x02
APP_START = 0xF4
HW_ID = 0x20
# Initialize I2C
i2c = I2C(0, scl=Pin(22), sda=Pin(21))
# Verify the sensor
hw_id = i2c.readfrom_mem(CCS811_ADDR, HW_ID, 1)
if hw_id[0] != 0x81:
print("CCS811 not found!")
while True:
pass
# Start the sensor
i2c.writeto(CCS811_ADDR, bytes([APP_START]))
time.sleep(0.1)
# Set measurement mode
i2c.writeto_mem(CCS811_ADDR, MEAS_MODE, bytes([0x10]))
def read_data():
data = i2c.readfrom_mem(CCS811_ADDR, ALG_RESULT_DATA, 8)
eCO2 = (data[0] << 8) | data[1]
TVOC = (data[2] << 8) | data[3]
return eCO2, TVOC
while True:
eCO2, TVOC = read_data()
print(f"eCO2: {eCO2} ppm, TVOC: {TVOC} ppb")
time.sleep(1)APP_START register, and configures the measurement mode. In the main loop, the script reads eCO₂ and TVOC values from the ALG_RESULT_DATA register and prints the results every second.Wrapping Up CCS811
The ESP32 CCS811 Digital Gas Sensor is a powerful Air Quality sensor that offers excellent performance and reliability. With support for multiple development platforms including Arduino, ESP-IDF, ESPHome, PlatformIO, and MicroPython, it's a versatile choice for your IoT projects.
Best Practices
For optimal performance, ensure proper wiring and follow the recommended configuration for your chosen development platform.
Safety First
Always verify power supply requirements and pin connections before powering up your project to avoid potential damage.
Ready to Start Building?
Now that you have all the information you need, it's time to integrate the CCS811 into your ESP32 project and bring your ideas to life!
Explore Alternative Sensors
Looking for alternatives to the CCS811? Check out these similar sensors that might fit your project needs.

AGS10 Sensor
The AGS10 is a gas sensor known for detecting a range of gases, including methane, propane, and hydrogen. Designed with stability and...
ENS160 Digital Metal-Oxide Multi-Gas Sensor
The ENS160 is a digital MOX gas sensor optimized for indoor air quality monitoring. It provides accurate measurements of TVOC and eCO₂...

Sharp GP2Y1010AU0F Optical Dust Sensor
The Sharp GP2Y1010AU0F is an optical dust sensor designed for air quality monitoring. It detects fine particles like cigarette smoke by...





