MH-Z19 NDIR CO₂ Sensor
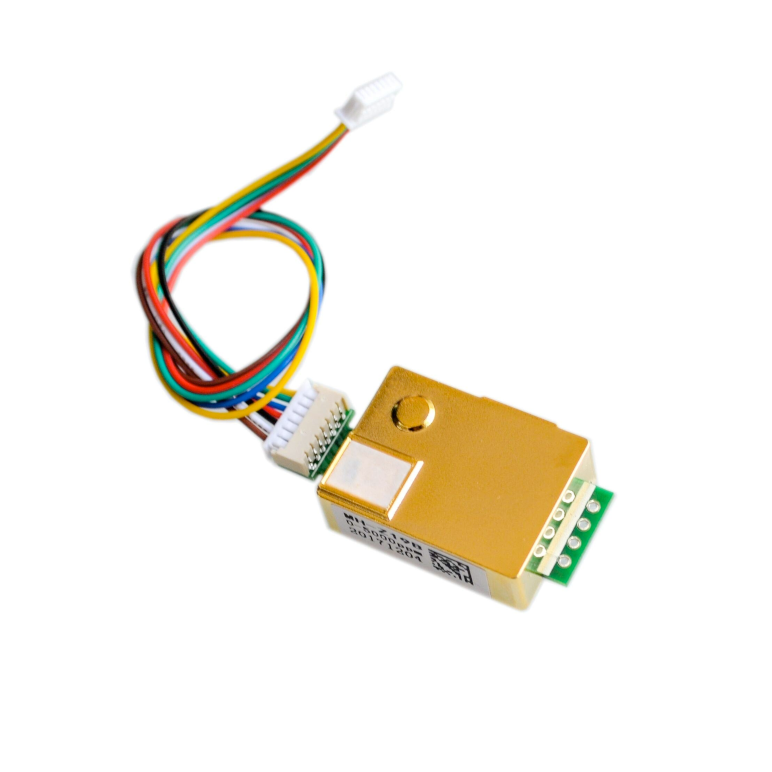

View on Amazon
Overview
About MH-Z19 NDIR CO₂ Sensor
The MH-Z19 is a Non-Dispersive Infrared (NDIR) CO₂ sensor designed for precise carbon dioxide (CO₂) measurement. With high sensitivity, selectivity, and a long lifespan, it is ideal for HVAC systems, indoor air quality monitoring, and industrial applications.
⚡ Key Features
- NDIR Technology – Ensures accurate CO₂ detection with minimal interference.
- Flexible Data Output – Supports both UART and PWM communication.
- Long Lifespan & High Stability – Reliable for continuous air quality monitoring.
- Ideal for Smart Air Quality Systems – Commonly used in HVAC, greenhouses, and CO₂ monitoring devices.
For VOC and multi-gas detection, consider the CCS811, which detects TVOCs and eCO₂. 🚀
The MH-Z19 offers a detection range of 0 to 2000 ppm (extendable to 5000 ppm upon request) with an accuracy of ±50 ppm + 5% of the reading. It also includes temperature compensation for reliable readings under varying environmental conditions. Compact in design, it is easy to integrate into a variety of projects.
Get Your MH-Z19



💡 Prices are subject to change. We earn from qualifying purchases as an Amazon Associate.
MH-Z19 Specifications
Complete technical specification details for MH-Z19 NDIR CO₂ Sensor
📊 Technical Parameters
MH-Z19 Pinout
The MH-Z19 has a 9-pin interface supporting UART communication and optional PWM output.
Visual Pinout Diagram
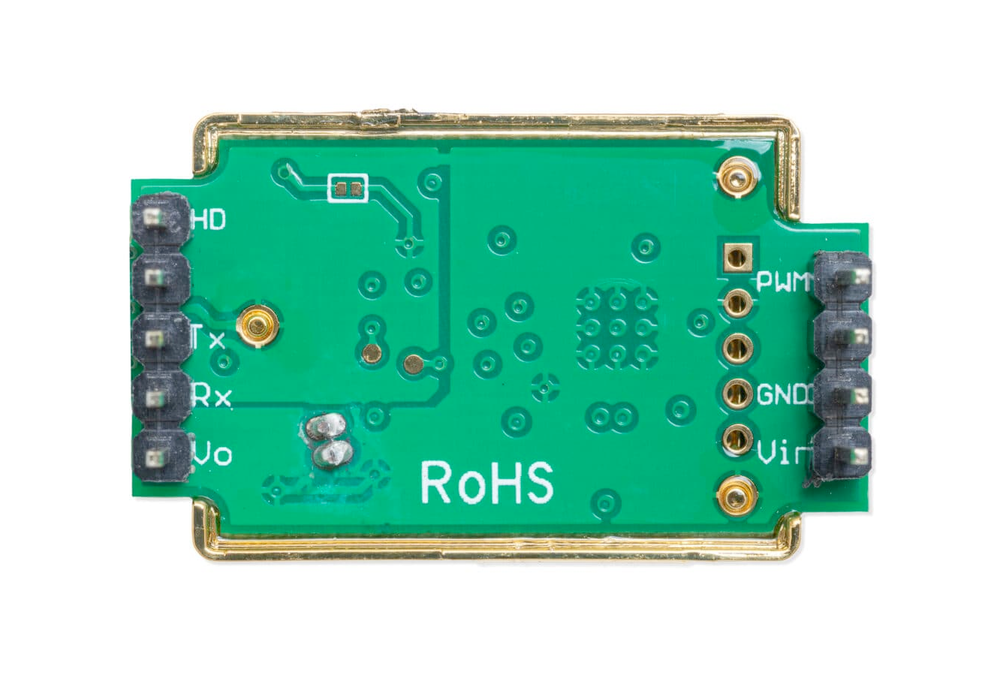
Pin Types
Quick Tips
Object],[object Object]
technology for accurate CO₂ measurement,Includes temperature compensation
Object]
Pin Descriptions
| Pin Name | Type | Description | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
1 Pin 1 (Vout) | Power | 3.3V output (max 10mA). Can power low-current 3.3V devices. | Not suitable for powering ESP32. |
2 Pin 2 (RXD) | UART | UART receive input (3.3V logic). Receives commands from microcontroller. | Connect to ESP32 TX pin. |
3 Pin 3 (TXD) | UART | UART transmit output (3.3V logic). Sends CO₂ data to microcontroller. | Connect to ESP32 RX pin. |
4 Pin 4 (SR) | Reserved | Factory reserved. Do not connect. | |
5 Pin 5 (HD) | Calibration | Zero calibration input. Pull low for >7 seconds to calibrate at 400ppm. | Use in fresh air environment for calibration. |
6 Pin 6 (Vin) | Power | Power supply input (3.6V-5.5V). Connect to 5V for optimal performance. | Requires stable power supply. |
7 Pin 7 (GND) | Power | Ground connection. Connect to system ground. | |
8 Pin 8 (AOT) | Reserved | Factory reserved. Do not connect. | |
9 Pin 9 (PWM) | PWM | PWM output for CO₂ concentration. Alternative to UART communication. | Optional - can use UART or PWM, not both. |
Wiring MH-Z19 to ESP32
To interface the MH-Z19 with an ESP32 via UART, connect Vin to 5V, GND to ground, TXD to ESP32 RX (GPIO 16), and RXD to ESP32 TX (GPIO 17).
Visual Wiring Diagram
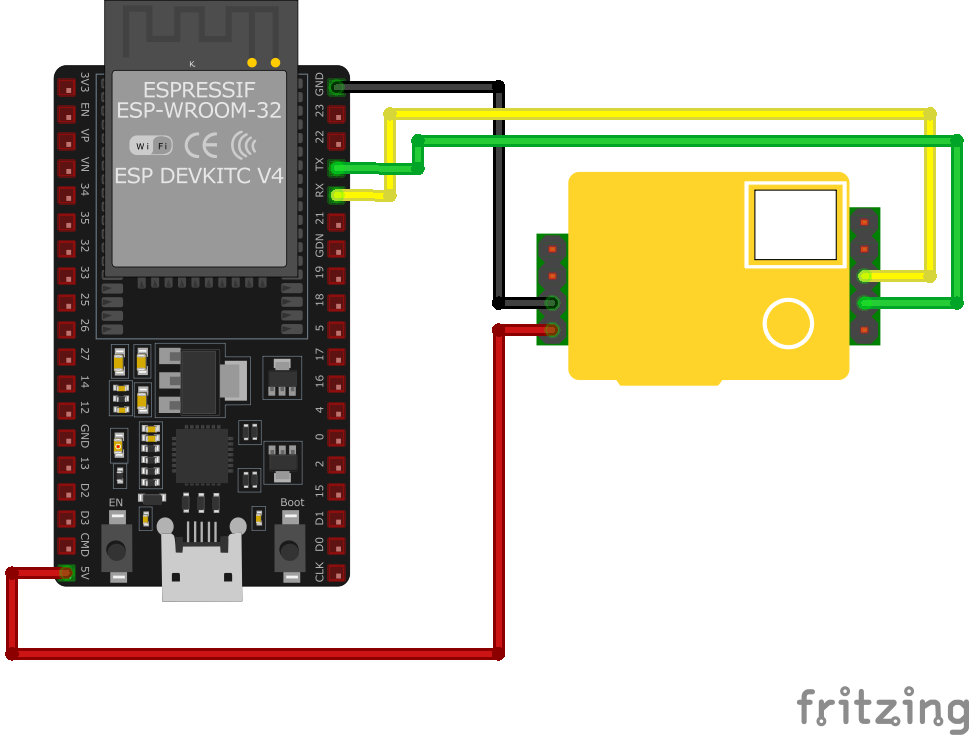
Connection Status
Protocol
Pin Connections
| MH-Z19 Pin | Connection | ESP32 Pin | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
1 Pin 6 (Vin) Required | 5V | Power supply (3.6V-5.5V). Use 5V for best performance. | |
2 Pin 7 (GND) Required | GND | Ground connection. | |
3 Pin 3 (TXD) Required | GPIO 16 (RX2) | Sensor transmits CO₂ data to ESP32. | |
4 Pin 2 (RXD) Required | GPIO 17 (TX2) | Sensor receives commands from ESP32. | |
5 Pin 5 (HD) Optional | Optional GPIO | Zero calibration trigger. Pull low for >7s in fresh air. |
Object]
3+ minutes warm-up time after power-on
in fresh air (~400ppm CO₂) for accuracy
has 3.3V logic levels - directly compatible with ESP32
level shifter if interfacing with 5V-only microcontrollers
Object]
MH-Z19 Troubleshooting
Common issues and solutions to help you get your sensor working
Common Issues
Issue: The MH-Z19 sensor fails to initialize, resulting in errors such as: MHZ19: Invalid preamble from MHZ19!.
Possible causes include incorrect wiring connections, incompatible serial communication settings, or insufficient power supply.
Solution: Verify that the sensor's TX and RX pins are correctly connected to the corresponding RX and TX pins on the microcontroller. Ensure that the serial communication parameters (baud rate, data bits, etc.) match between the sensor and the microcontroller. Provide a stable 5V power supply to the sensor, as it requires 4.5V to 5.5V for proper operation.
Issue: The sensor outputs a constant high CO2 concentration value, such as 5000 ppm, which is the maximum measurable value.
Possible causes include sensor calibration issues, exposure to high concentrations of CO2 during startup, or faulty sensor hardware.
Solution: Perform a zero-point calibration in a fresh air environment (approximately 400 ppm CO2) to reset the sensor's baseline. Ensure the sensor is exposed to clean air during initialization to prevent incorrect baseline calibration. If the issue persists, consider replacing the sensor, as it may be defective.
🌡️ Inaccurate CO2 Readings
Issue: The MH-Z19 sensor provides CO2 readings that are significantly higher or lower than expected.
Possible causes include incorrect calibration, interference from other gases, or environmental factors.
Solution: Check the sensor's calibration status and perform a manual calibration if necessary. Place the sensor in an environment with clean air to establish a proper baseline. Avoid placing the sensor near sources of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) or other gases that may interfere with CO2 measurements.
Issue: Serial communication with the MH-Z19 sensor fails, resulting in errors such as: Timeout waiting for response.
Possible causes include incorrect baud rate settings, reversed TX/RX connections, or noisy serial lines.
Solution: Confirm the baud rate used by the sensor (typically 9600 or 19200) and match it with the microcontroller's serial port settings. Double-check the TX and RX connections to ensure they are not swapped. Use short, high-quality cables to minimize noise on the serial lines.
Debugging Tips
Use the Serial Monitor to check for error messages and verify the sensor's output. Add debug prints in your code to track the sensor's state.
Use a multimeter to verify voltage levels and check for continuity in your connections. Ensure the power supply is stable and within the sensor's requirements.
Additional Resources
MH-Z19 Programming Examples
Ready-to-use code examples for different platforms and frameworks
#include <SoftwareSerial.h>
SoftwareSerial mySerial(10, 11); // RX, TX
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
mySerial.begin(9600);
}
void loop() {
byte cmd[9] = {0xFF, 0x01, 0x86, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x79};
mySerial.write(cmd, 9);
delay(500);
if (mySerial.available()) {
byte response[9];
mySerial.readBytes(response, 9);
if (response[0] == 0xFF && response[1] == 0x86) {
int CO2 = (response[2] << 8) + response[3];
Serial.print("CO2 Concentration: ");
Serial.print(CO2);
Serial.println(" ppm");
}
}
delay(2000);
}#include <stdio.h>
#include "driver/uart.h"
#include "freertos/FreeRTOS.h"
#include "freertos/task.h"
#define UART_NUM UART_NUM_1
#define TXD_PIN (GPIO_NUM_17)
#define RXD_PIN (GPIO_NUM_16)
void app_main(void) {
const uart_config_t uart_config = {
.baud_rate = 9600,
.data_bits = UART_DATA_8_BITS,
.parity = UART_PARITY_DISABLE,
.stop_bits = UART_STOP_BITS_1,
.flow_ctrl = UART_HW_FLOWCTRL_DISABLE
};
uart_param_config(UART_NUM, &uart_config);
uart_set_pin(UART_NUM, TXD_PIN, RXD_PIN, UART_PIN_NO_CHANGE, UART_PIN_NO_CHANGE);
uart_driver_install(UART_NUM, 256, 0, 0, NULL, 0);
uint8_t cmd[9] = {0xFF, 0x01, 0x86, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x79};
uint8_t response[9];
while (1) {
uart_write_bytes(UART_NUM, (const char *)cmd, 9);
vTaskDelay(pdMS_TO_TICKS(500));
int len = uart_read_bytes(UART_NUM, response, 9, pdMS_TO_TICKS(1000));
if (len == 9 && response[0] == 0xFF && response[1] == 0x86) {
int CO2 = (response[2] << 8) | response[3];
printf("CO2 Concentration: %d ppm\n", CO2);
}
vTaskDelay(pdMS_TO_TICKS(2000));
}
}uart:
tx_pin: GPIO17
rx_pin: GPIO16
baud_rate: 9600
sensor:
- platform: mhz19
co2:
name: "MH-Z19 CO2"
temperature:
name: "MH-Z19 Temperature"
update_interval: 60splatformio.ini
[env:esp32dev]
platform = espressif32
board = esp32dev
framework = arduino
monitor_speed = 115200main.cpp
#include <MHZ19.h>
#include <SoftwareSerial.h>
SoftwareSerial mySerial(16, 17); // RX, TX
MHZ19 myMHZ19;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
mySerial.begin(9600);
myMHZ19.begin(mySerial);
myMHZ19.autoCalibration();
}
void loop() {
int co2 = myMHZ19.getCO2();
float temp = myMHZ19.getTemperature();
if (co2 > 0) {
Serial.print("CO2 Concentration: ");
Serial.print(co2);
Serial.println(" ppm");
} else {
Serial.println("Error reading CO2 concentration");
}
Serial.print("Temperature: ");
Serial.print(temp);
Serial.println(" °C");
delay(5000);
}from machine import UART, Pin
import time
uart = UART(2, baudrate=9600, tx=Pin(17), rx=Pin(16))
cmd = bytearray([0xFF, 0x01, 0x86, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x79])
def read_co2():
uart.write(cmd)
time.sleep(0.1)
if uart.any():
response = uart.read(9)
if len(response) == 9 and response[0] == 0xFF and response[1] == 0x86:
co2 = (response[2] << 8) | response[3]
return co2
return None
while True:
co2 = read_co2()
if co2 is not None:
print(f"CO2 Concentration: {co2} ppm")
else:
print("Error reading CO2 concentration")
time.sleep(2)Wrapping Up MH-Z19
The ESP32 MH-Z19 NDIR CO₂ Sensor is a powerful Air Quality sensor that offers excellent performance and reliability. With support for multiple development platforms including Arduino, ESP-IDF, ESPHome, PlatformIO, and MicroPython, it's a versatile choice for your IoT projects.
Best Practices
For optimal performance, ensure proper wiring and follow the recommended configuration for your chosen development platform.
Safety First
Always verify power supply requirements and pin connections before powering up your project to avoid potential damage.
Ready to Start Building?
Now that you have all the information you need, it's time to integrate the MH-Z19 into your ESP32 project and bring your ideas to life!
Explore Alternative Sensors
Looking for alternatives to the MH-Z19? Check out these similar sensors that might fit your project needs.
CCS811 Digital Gas Sensor
The CCS811 is a digital gas sensor for monitoring indoor air quality. It measures levels of Total Volatile Organic Compounds (TVOCs) and...

Sharp GP2Y1010AU0F Optical Dust Sensor
The Sharp GP2Y1010AU0F is an optical dust sensor designed for air quality monitoring. It detects fine particles like cigarette smoke by...

AGS10 Sensor
The AGS10 is a gas sensor known for detecting a range of gases, including methane, propane, and hydrogen. Designed with stability and...





