SIM800A GSM/GPRS Module

View on Amazon
Overview
About SIM800A GSM/GPRS Module
The SIM800A is a compact GSM/GPRS module designed for voice, SMS, and data transmission over dual-band (900/1800MHz) networks. With its small size and low power consumption, it is an excellent choice for wearables, IoT devices, and industrial automation.
⚡ Key Features
- Dual-Band GSM (900/1800MHz) – Ensures reliable connectivity in supported regions.
- Versatile Communication – Supports voice calls, SMS, and GPRS data transfer.
- Multiple Interfaces – Includes UART and USB for seamless integration.
- Compact & Low Power – Ideal for battery-powered and space-constrained applications.
🔗 Still deciding on a SIM module? Check the ESP32 SIM Modules Comparison Table for a breakdown of LTE, 3G, and GPRS options. 🚀
Get Your SIM800A



Prices are subject to change. We earn from qualifying purchases as an Amazon Associate.
SIM800A Specifications
Complete technical specification details for SIM800A GSM/GPRS Module
📊 Technical Parameters
SIM800A Pinout
The SIM800A pinout includes power, UART communication, control, status indication, antenna connection, and SIM card interface pins for quad-band GSM/GPRS connectivity.
Visual Pinout Diagram
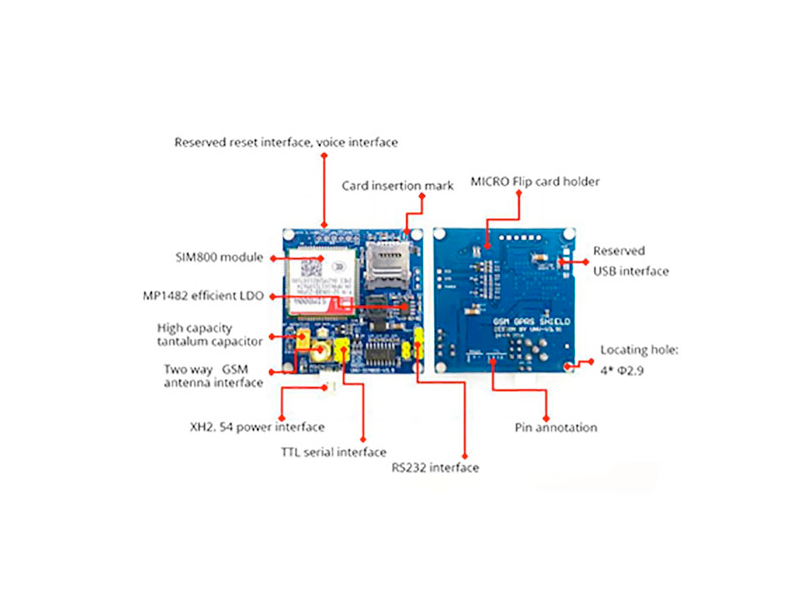
Pin Types
Quick Tips
GSM/GPRS module (850/900/1800/1900MHz),Supports voice calls, SMS, and GPRS data transfer,GPRS multi-slot class 12/10
mobile station class B,Requires SIM card for cellular connectivity
consumption: 2A peak during transmission,Default baud rate: 9600 bps (configurable via AT commands)
Pin Descriptions
| Pin Name | Type | Description | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
1 VBAT | Power | Power supply input (3.4V to 4.4V) | Requires stable power supply with peak current up to 2A |
2 GND | Ground | Ground connection | Connect to common ground |
3 TXD | UART TX | UART Transmit Data (connects to microcontroller RX) | Default baud rate: 9600 bps |
4 RXD | UART RX | UART Receive Data (connects to microcontroller TX) | Default baud rate: 9600 bps |
5 PWRKEY | Control | Power on/off control (active low) | Pull low for at least 1 second to power on |
6 RST | Control | Module reset (active low) | Pull low to reset the module |
7 NETLIGHT | Status | Network status indication | LED indicator for network registration status |
8 ANT | Antenna | Antenna connection | Requires external GSM antenna |
Wiring SIM800A to ESP32
Connect the SIM800A to your ESP32 via UART for AT command communication. The module requires a stable 3.4V-4.4V power supply with sufficient current capacity (peak 2A). An external GSM antenna is required for network connectivity.
Visual Wiring Diagram
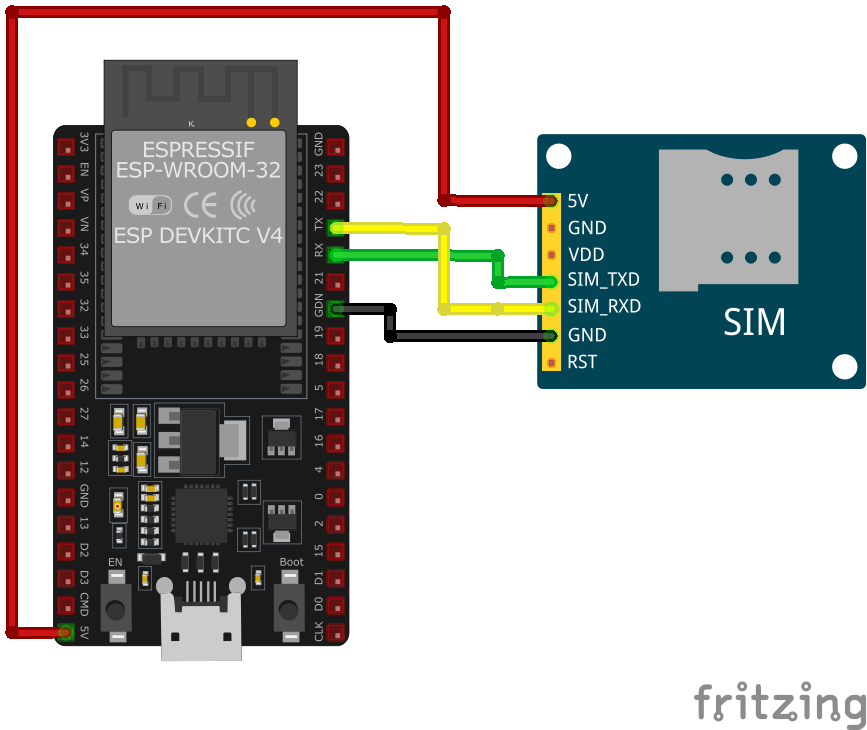
Connection Status
Protocol
Pin Connections
| SIM800A Pin | Connection | ESP32 Pin | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
1 VBAT Required | 3.7V-4.4V Power Supply | Provide stable power (NOT from ESP32 pin) | |
2 GND Required | GND | Common ground connection | |
3 TXD Required | GPIO16 (RX2) | SIM800A TX to ESP32 RX | |
4 RXD Required | GPIO17 (TX2) | SIM800A RX to ESP32 TX | |
5 PWRKEY Optional | GPIO4 | Power control (pull low to power on) | |
6 RST Optional | GPIO5 | Module reset control | |
7 ANT Required | External GSM Antenna | Connect GSM antenna |
CRITICAL: Use a dedicated power supply (3.4V-4.4V, 2A peak) - DO NOT power from ESP32 pin!
UART baud rate is 9600 bps
logic level shifters if needed (though ESP32 is 3.3V compatible)
GSM antenna is mandatory for network connectivity
PWRKEY low for at least 1 second to power on the module
NETLIGHT pin for network registration status
active SIM card before powering on
good antenna placement for optimal signal reception
SIM800A Troubleshooting
Common issues and solutions to help you get your sensor working
Common Issues
Issue: The SIM800A module does not power up or respond to commands.
Possible causes include insufficient power supply, incorrect wiring, or faulty hardware.
Solution: Ensure the module is connected to a stable power source within the recommended voltage range of 3.4V to 4.4V. Verify that all connections are secure and correctly configured. If the problem persists, consider testing the module with a different power source or replacing it.
Issue: The module fails to detect or register the SIM card.
Possible causes include improper SIM card insertion, unsupported SIM card type, or SIM card lock.
Solution: Ensure the SIM card is properly inserted into the module's SIM card slot and is compatible with the GSM network. Verify that the SIM card is active and unlocked. If necessary, test the SIM card in another device to confirm its functionality.
Issue: The module experiences weak signal strength or fails to maintain a stable network connection.
Possible causes include improper antenna connection, environmental interference, or network coverage limitations.
Solution: Ensure the GSM antenna is securely connected to the module and positioned for optimal signal reception. Avoid placing the module near sources of electromagnetic interference. Check the network coverage in your area to ensure adequate signal strength.
Issue: The module does not respond to AT commands sent from the microcontroller or computer.
Possible causes include incorrect baud rate settings, faulty serial connections, or improper command syntax.
Solution: Verify that the baud rate of the module matches that of the microcontroller or computer; the default baud rate is 9600 bps. Check that the TX and RX lines are correctly connected and that there are no loose connections. Ensure that AT commands are correctly formatted and terminated with a carriage return.
Issue: The SIM800A module becomes excessively hot during operation.
Possible causes include overvoltage, excessive current draw, or continuous high-power transmission.
Solution: Confirm that the power supply voltage is within the recommended range (3.4V to 4.4V). Monitor the current consumption to ensure it does not exceed the module's specifications. If the module is transmitting continuously, consider implementing power-saving modes or reducing the transmission frequency to prevent overheating.
Debugging Tips
Use the Serial Monitor to check for error messages and verify the sensor's output. Add debug prints in your code to track the sensor's state.
Use a multimeter to verify voltage levels and check for continuity in your connections. Ensure the power supply is stable and within the sensor's requirements.
Additional Resources
SIM800A Programming Examples
Ready-to-use code examples for different platforms and frameworks
#include <SoftwareSerial.h>
SoftwareSerial sim800a(10, 11); // RX, TX
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
sim800a.begin(9600);
// Power on the module
pinMode(9, OUTPUT);
digitalWrite(9, LOW);
delay(1000); // PWRKEY needs to be low for at least 1 second
digitalWrite(9, HIGH);
delay(5000); // Wait for the module to initialize
// Test AT communication
sim800a.println("AT");
delay(1000);
while (sim800a.available()) {
Serial.write(sim800a.read());
}
}
void loop() {
// Send an SMS
sim800a.println("AT+CMGF=1"); // Set SMS to text mode
delay(1000);
sim800a.println("AT+CMGS=\"+1234567890\""); // Replace with recipient's number
delay(1000);
sim800a.print("Hello from SIM800A");
delay(1000);
sim800a.write(26); // CTRL+Z to send SMS
delay(5000);
}#include <stdio.h>
#include "driver/uart.h"
#include "driver/gpio.h"
#include "freertos/task.h"
#define TX_PIN 17
#define RX_PIN 16
#define PWRKEY_PIN 4
#define UART_PORT UART_NUM_1
void init_uart() {
uart_config_t uart_config = {
.baud_rate = 9600,
.data_bits = UART_DATA_8_BITS,
.parity = UART_PARITY_DISABLE,
.stop_bits = UART_STOP_BITS_1,
.flow_ctrl = UART_HW_FLOWCTRL_DISABLE
};
uart_param_config(UART_PORT, &uart_config);
uart_set_pin(UART_PORT, TX_PIN, RX_PIN, UART_PIN_NO_CHANGE, UART_PIN_NO_CHANGE);
uart_driver_install(UART_PORT, 1024, 0, 0, NULL, 0);
}
void power_on_sim800a() {
gpio_set_direction(PWRKEY_PIN, GPIO_MODE_OUTPUT);
gpio_set_level(PWRKEY_PIN, 0);
vTaskDelay(1000 / portTICK_PERIOD_MS); // Hold PWRKEY low for 1 second
gpio_set_level(PWRKEY_PIN, 1);
vTaskDelay(5000 / portTICK_PERIOD_MS); // Wait for the module to initialize
}
void app_main(void) {
init_uart();
power_on_sim800a();
char *test_cmd = "AT\r\n";
uart_write_bytes(UART_PORT, test_cmd, strlen(test_cmd));
while (true) {
char data[128];
int len = uart_read_bytes(UART_PORT, data, sizeof(data), 100 / portTICK_PERIOD_MS);
if (len > 0) {
data[len] = '\0';
printf("Response: %s\n", data);
}
vTaskDelay(1000 / portTICK_PERIOD_MS);
}
}uart:
tx_pin: GPIO17
rx_pin: GPIO16
baud_rate: 9600
switch:
- platform: gpio
name: "SIM800A Power"
pin:
number: GPIO4
inverted: true
switch:
- platform: template
name: "Send AT Command"
turn_on_action:
- uart.write: "AT\r\n"
sensor:
- platform: custom
lambda: |-
return {nullptr};
sensors:
- name: "SIM800A Response"platformio.ini
[env:sim800a]
platform = espressif32
board = esp32dev
framework = arduino
monitor_speed = 115200main.cpp
#include <HardwareSerial.h>
#include <Arduino.h>
HardwareSerial sim800a(1);
#define PWRKEY 4
void power_on_sim800a() {
pinMode(PWRKEY, OUTPUT);
digitalWrite(PWRKEY, LOW);
delay(1000); // Hold PWRKEY low for 1 second
digitalWrite(PWRKEY, HIGH);
delay(5000); // Wait for initialization
}
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
sim800a.begin(9600, SERIAL_8N1, 16, 17); // RX, TX
power_on_sim800a();
// Test AT command
sim800a.println("AT");
delay(1000);
while (sim800a.available()) {
Serial.write(sim800a.read());
}
}
void loop() {
sim800a.println("AT+CMGF=1"); // Set SMS to text mode
delay(1000);
sim800a.println("AT+CMGS=\"+1234567890\""); // Replace with recipient's number
delay(1000);
sim800a.print("Hello from PlatformIO");
delay(1000);
sim800a.write(26); // CTRL+Z to send SMS
delay(5000);
}from machine import UART, Pin
import time
# Initialize UART
uart = UART(2, baudrate=9600, tx=17, rx=16)
pwrkey = Pin(4, Pin.OUT)
def power_on_sim800a():
pwrkey.value(0)
time.sleep(1) # Hold PWRKEY low for 1 second
pwrkey.value(1)
time.sleep(5) # Wait for module to initialize
def send_at(command):
uart.write(command + '\r\n')
time.sleep(1)
while uart.any():
print(uart.read().decode('utf-8'), end='')
# Power on the module
power_on_sim800a()
# Test communication
send_at('AT')
# Send SMS
send_at('AT+CMGF=1') # Set SMS to text mode
send_at('AT+CMGS="+1234567890"') # Replace with recipient's number
uart.write("Hello from MicroPython" + chr(26))Wrapping Up SIM800A
The ESP32 SIM800A GSM/GPRS Module is a powerful SIM sensor that offers excellent performance and reliability. With support for multiple development platforms including Arduino, ESP-IDF, ESPHome, PlatformIO, and MicroPython, it's a versatile choice for your IoT projects.
Best Practices
For optimal performance, ensure proper wiring and follow the recommended configuration for your chosen development platform.
Safety First
Always verify power supply requirements and pin connections before powering up your project to avoid potential damage.
Ready to Start Building?
Now that you have all the information you need, it's time to integrate the SIM800A into your ESP32 project and bring your ideas to life!
Explore Alternative Sensors
Looking for alternatives to the SIM800A? Check out these similar sensors that might fit your project needs.
The SIM900 is a versatile GSM/GPRS module that provides reliable communication capabilities for various applications. Its compact design and...
The SIM7600G is a versatile LTE CAT1 module that provides reliable communication capabilities for various IoT applications. Its compact...








