VL6180X Time-of-Flight Sensor
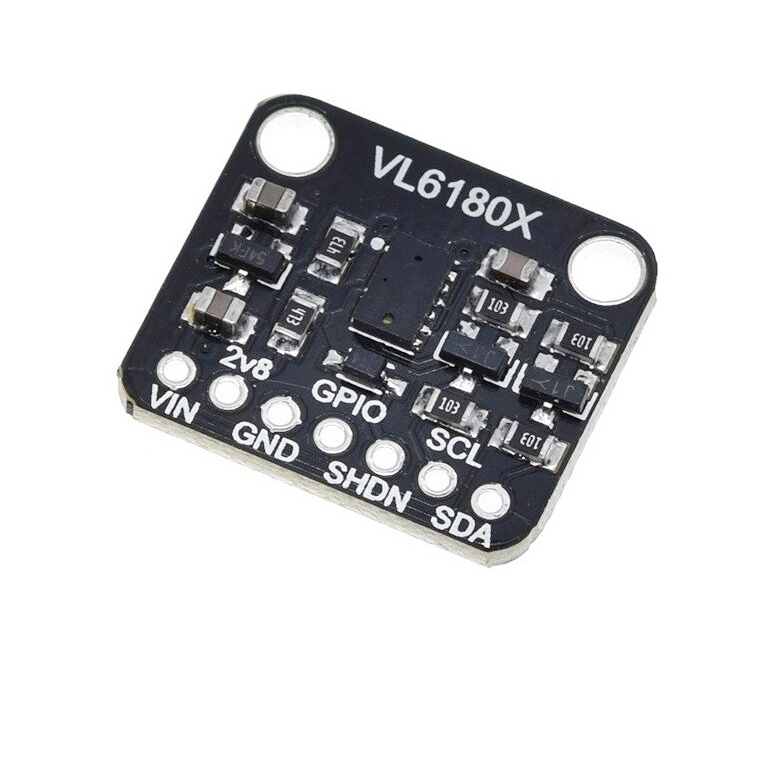

View on Amazon
Overview
About VL6180X Time-of-Flight Sensor
📏 VL6180X Sensor Overview
- Range: 0cm to 50cm (Max)
- Interface: I²C digital communication
- Resolution: 1mm precision
- Field of View: 25°
- Operating Voltage: 2.8V to 5V (via onboard regulator)
- Typical Current: ~20–30mA
- Wavelength: 850nm IR
- Integrated Ambient Light Sensor
Get Your VL6180X



💡 Prices are subject to change. We earn from qualifying purchases as an Amazon Associate.
VL6180X Pinout
The VL6180X pinout includes I2C communication pins (SDA, SCL), power supply (VIN, GND), shutdown pin (SHDN), interrupt pin (GPIO), and 2.8V regulator output for short-range proximity sensing and ambient light detection.
Visual Pinout Diagram
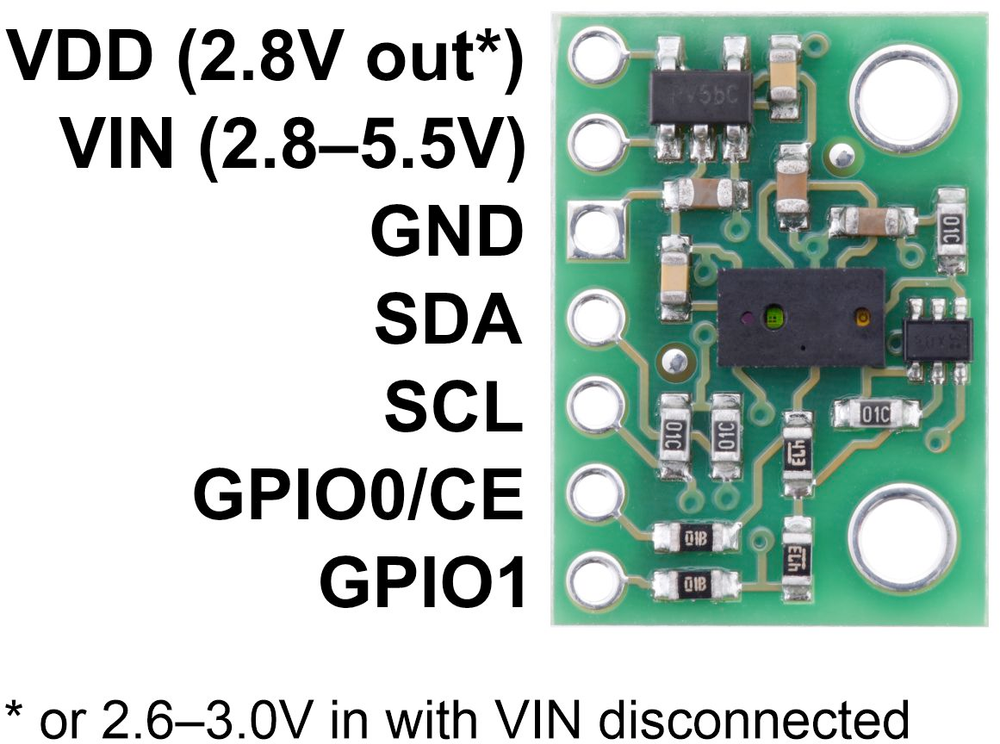
Pin Types
Quick Tips
Time-of-Flight (ToF) proximity sensor,Measurement range: 0 mm to 200 mm (20 cm max),Resolution: 1 mm precision,Field of View: 25°
voltage: 2.8V to 5V (via onboard regulator),3-in-1 system: IR emitter, sensor, and ranging processor,Integrated ambient light sensor (ALS)
address: 0x29 (default),IR wavelength: 850 nm,Current consumption: ~20-30 mA during operation
Pin Descriptions
| Pin Name | Type | Description | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
1 VIN | Power | Power supply input (2.8V to 5V) | Onboard regulator supports wide voltage |
2 GND | Ground | Ground connection | Common ground |
3 SDA | I2C Data | I2C Serial Data line | Bidirectional data (requires pull-up) |
4 SCL | I2C Clock | I2C Serial Clock line | Clock signal (requires pull-up) |
5 SHDN | Control | Shutdown pin (active low) | Tie high to enable sensor |
6 GPIO | Interrupt | Interrupt or general I/O pin | Optional for interrupts or alerts |
7 2v8 | Power Out | Regulated 2.8V output | Can power external components |
Wiring VL6180X to ESP32
Connect the VL6180X to your ESP32 via I2C (SDA and SCL pins). This sensor combines short-range ToF distance measurement (up to 20 cm) with an integrated ambient light sensor. The onboard regulator accepts 2.8V to 5V input.
Visual Wiring Diagram
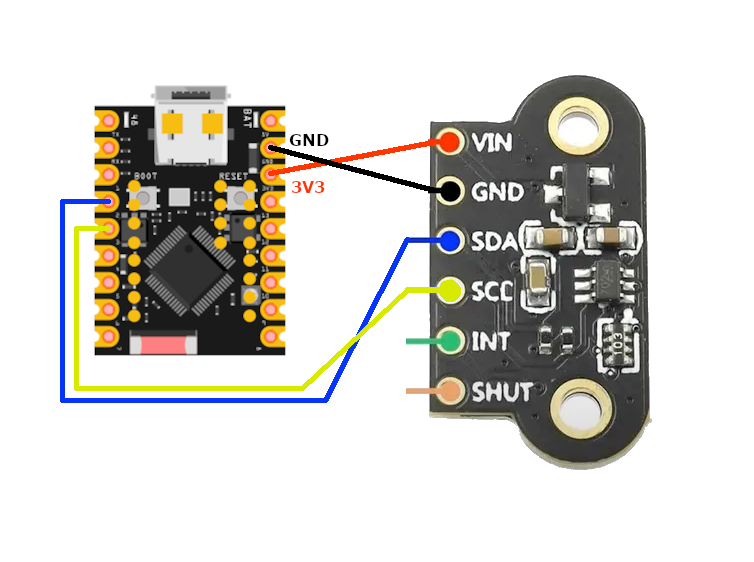
Connection Status
Protocol
Pin Connections
| VL6180X Pin | Connection | ESP32 Pin | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
1 VIN Required | 3.3V or 5V | Power supply (2.8V to 5V) | |
2 GND Required | GND | Ground connection | |
3 SDA Required | GPIO21 | I2C data line (with pull-up) | |
4 SCL Required | GPIO22 | I2C clock line (with pull-up) | |
5 SHDN Optional | 3.3V or GPIO | Shutdown control (tie high to enable) | |
6 GPIO Optional | GPIO (optional) | Interrupt/alert output |
sensor: 0-20 cm (best for proximity detection)
address: 0x29 (same as VL53L0X and VL53L1X)
ambient light sensor (ALS) for light measurement
regulator: 2.8V to 5V input (flexible power)
pin provides regulated 2.8V output
resistors typically included on module
pin: Tie high (3.3V/5V) to enable sensor
pin can signal measurement ready or threshold alerts
Adafruit_VL6180X library for Arduino/ESP32
for gesture recognition and presence detection
in close-range applications than VL53L0X
nm IR wavelength (different from VL53 series 940 nm)
VL6180X Troubleshooting
Common issues and solutions to help you get your sensor working
Common Issues
Issue: Sensor not responding or Adafruit library cannot detect it.
Solution: Verify wiring, power level, and ensure SHDN is pulled high.
Issue: Only returns 0mm or 50mm constantly.
Solution: Ensure target is in range and sensor is facing it directly. Check for surface reflectivity.
Issue: Fluctuating or erratic readings.
Solution: Use a clean 3.3V/5V supply and decoupling capacitor. Avoid connecting SHDN to a floating pin.
Debugging Tips
Use the Serial Monitor to check for error messages and verify the sensor's output. Add debug prints in your code to track the sensor's state.
Use a multimeter to verify voltage levels and check for continuity in your connections. Ensure the power supply is stable and within the sensor's requirements.
Additional Resources
VL6180X Programming Examples
Ready-to-use code examples for different platforms and frameworks
Wrapping Up VL6180X
The ESP32 VL6180X Time-of-Flight Sensor is a powerful distance sensor that offers excellent performance and reliability. With support for multiple development platforms including Arduino, ESP-IDF, ESPHome, PlatformIO, and MicroPython, it's a versatile choice for your IoT projects.
Best Practices
For optimal performance, ensure proper wiring and follow the recommended configuration for your chosen development platform.
Safety First
Always verify power supply requirements and pin connections before powering up your project to avoid potential damage.
Ready to Start Building?
Now that you have all the information you need, it's time to integrate the VL6180X into your ESP32 project and bring your ideas to life!
Explore Alternative Sensors
Looking for alternatives to the VL6180X? Check out these similar sensors that might fit your project needs.
VL53L0X V2 Time-of-Flight Sensor
The VL53L0X V2 (GY-VL53L0XV2) is a high-accuracy Time-of-Flight (ToF) laser ranging sensor that can measure distances up to 2 meters. It's...

TOF400C Time-of-Flight Sensor
The TOF400C is a long-range laser-based time-of-flight (ToF) sensor based on the VL53L1X chip from STMicroelectronics. It measures distances...

VL53L1X Time-of-Flight Sensor
The VL53L1X is a high-accuracy long-distance laser-ranging sensor from STMicroelectronics. It uses a 940nm VCSEL emitter and advanced SPAD...
