ESP32 BMP085 Barometric Pressure Sensor Pinout, Wiring and more
Overview
The BMP085 is a high-precision digital barometric pressure and temperature sensor, ideal for weather monitoring, altimetry, and navigation. It uses an I²C interface for communication and offers low power consumption, making it suitable for battery-powered devices.
About BMP085 Barometric Pressure Sensor
The BMP085, developed by Bosch Sensortec, is a high-accuracy barometric pressure sensor designed for weather monitoring, altimetry, and GPS enhancement. With a wide pressure range and I²C communication, it is ideal for altitude tracking and environmental sensing.
⚡ Key Features
- Accurate Barometric Pressure Sensing – Measures 300 hPa to 1100 hPa, covering -500 to 9000 meters altitude.
- Integrated Temperature Sensor – Enables altitude and weather compensation.
- I²C Communication – Simple integration with ESP32, Arduino, and other microcontrollers.
- Compact & Low Power – Ideal for portable and battery-powered applications.
With its precision and reliability, the BMP085 is a great choice for weather stations, drones, and altitude-based applications. 🚀
BMP085 Datasheet and Technical Specifications
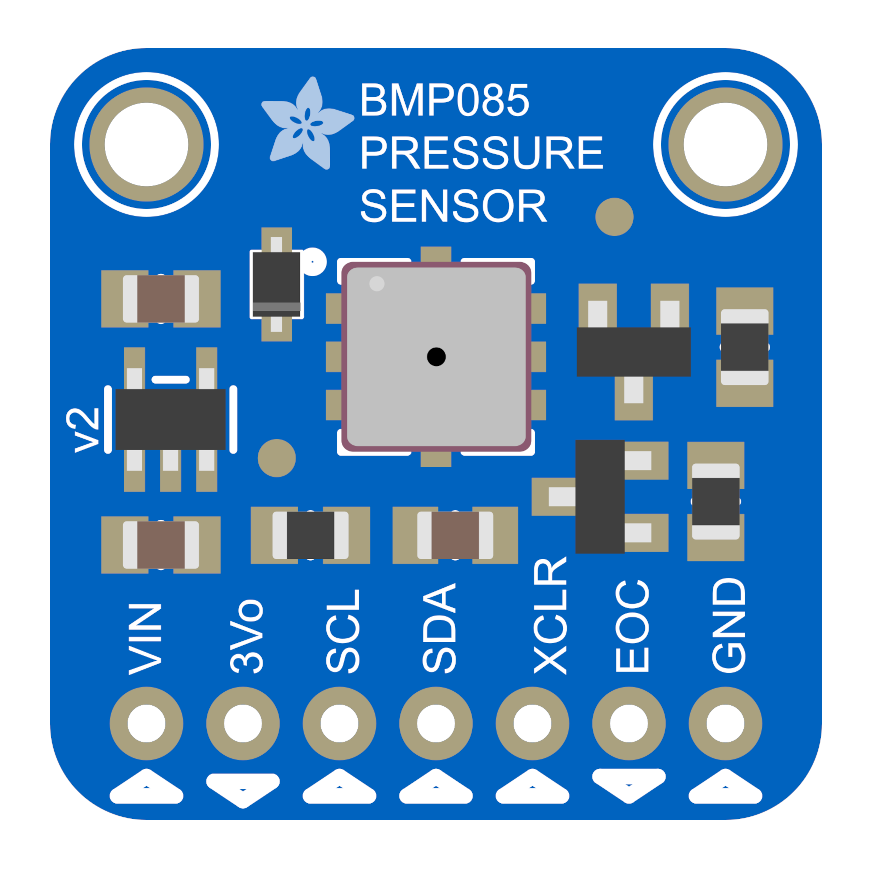
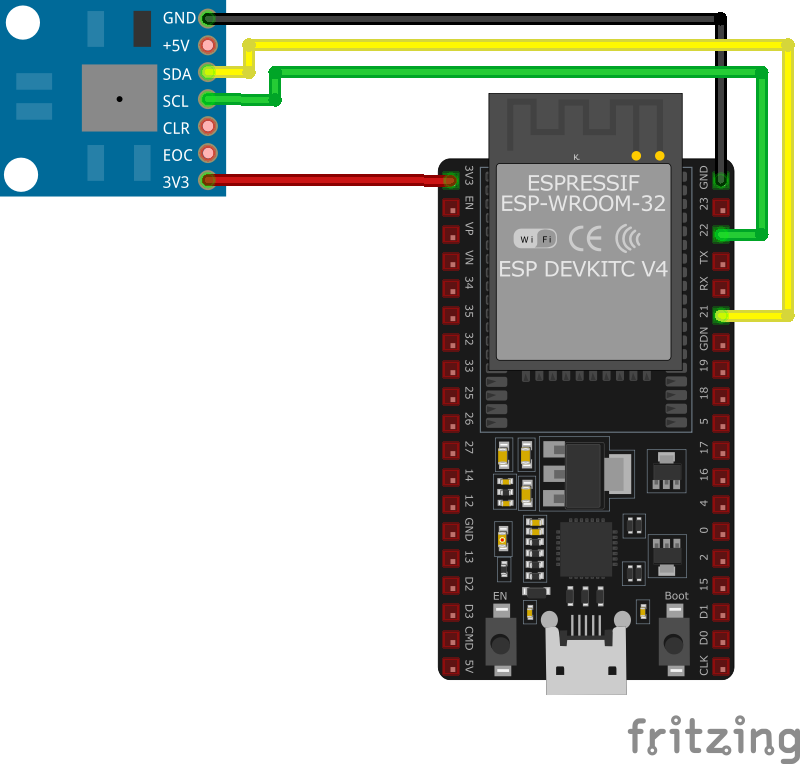
BMP085 Pinout Diagram
The VCC pin is used to supply power to the sensor, and it typically requires 3.3V or 5V (refer to the datasheet for specific voltage requirements). The GND pin is the ground connection and must be connected to the ground of your ESP32.
The BMP085 module has the following pins: VIN: Supplies power to the module, typically 3.3V or 5V. GND: Ground pin for the module. SDA: Serial Data pin for I2C communication. Connect to the microcontroller's SDA pin. SCL: Serial Clock pin for I2C communication. Connect to the microcontroller's SCL pin.
BMP085 Troubleshooting Guide
Common Issues
💻 Compilation Error: 'Adafruit_BMP085' does not name a type
Issue: When compiling code that utilizes the Adafruit BMP085 library, the following error occurs: 'Adafruit_BMP085' does not name a type.
Possible causes include incorrect installation of the library or mismatched library versions.
Solution: Ensure that the Adafruit BMP085 library is correctly installed in the Arduino IDE. Verify that the library folder is placed in the 'libraries' directory of your Arduino sketchbook and that the folder name does not contain hyphens or other special characters. Restart the Arduino IDE after installing the library to ensure it is recognized. Additionally, confirm that the example code matches the installed library version, as discrepancies can lead to such errors. (forums.adafruit.com)
❌ Sensor Initialization Failure: 'Could not find a valid BMP085 sensor'
Issue: The BMP085 sensor fails to initialize, and the serial monitor displays: Could not find a valid BMP085 sensor, check wiring!.
Possible causes include incorrect wiring, improper power supply, or issues with the I2C communication.
Solution: Verify that the sensor's SDA and SCL lines are correctly connected to the corresponding pins on the microcontroller. Ensure that the sensor is powered with the appropriate voltage (3.3V or 5V, depending on the sensor's specifications). Use an I2C scanner to detect the sensor's address; if the sensor is not found, check for loose connections or potential damage to the sensor. Additionally, confirm that the correct I2C address is specified in your code, as some BMP085 modules may use different default addresses. (community.particle.io)
🐍 Python Error: 'IOError: [Errno 5] Input/output error'
Issue: When interfacing the BMP085 sensor with a Raspberry Pi using Python, the following error is encountered: IOError: [Errno 5] Input/output error.
Possible causes include incorrect I2C setup, wiring issues, or conflicts with other I2C devices.
Solution: Ensure that I2C is enabled on the Raspberry Pi and that the necessary Python libraries for I2C communication are installed. Verify that the sensor's connections are secure and correspond to the correct GPIO pins. If multiple I2C devices are connected, check for address conflicts and ensure each device has a unique address. Using the 'i2cdetect' command can help identify connected devices and their addresses. (forums.raspberrypi.com)
⚠️ Incorrect Altitude Calculations Due to Pressure Readings
Issue: Altitude calculations based on BMP085 pressure readings are inaccurate, leading to erroneous altitude values.
Possible causes include incorrect pressure-to-altitude conversion formulas or uncalibrated sea-level pressure references.
Solution: Use the standard barometric formula to convert pressure readings to altitude, ensuring that the sea-level pressure reference is accurate for your location. Regularly updating the sea-level reference can improve accuracy. Additionally, consider using libraries that handle these calculations and calibrations automatically. (forum.microchip.com)
Debugging Tips
🔍 Serial Monitor
Use the Serial Monitor to check for error messages and verify the sensor's output. Add debug prints in your code to track the sensor's state.
⚡ Voltage Checks
Use a multimeter to verify voltage levels and check for continuity in your connections. Ensure the power supply is stable and within the sensor's requirements.
Additional Resources
BMP085 Code Examples
Arduino Example
#include <Wire.h>
#include <Adafruit_Sensor.h>
#include <Adafruit_BMP085_U.h>
Adafruit_BMP085_Unified bmp = Adafruit_BMP085_Unified(10085);
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
if (!bmp.begin()) {
Serial.println("Could not find a valid BMP085 sensor, check wiring!");
while (1);
}
}
void loop() {
sensors_event_t event;
bmp.getEvent(&event);
if (event.pressure) {
Serial.print("Pressure: ");
Serial.print(event.pressure);
Serial.println(" hPa");
}
float temperature;
bmp.getTemperature(&temperature);
Serial.print("Temperature: ");
Serial.print(temperature);
Serial.println(" *C");
delay(2000);
}This Arduino code initializes the BMP085 sensor using the Adafruit_BMP085_Unified library. In the loop() function, the code reads and prints atmospheric pressure and temperature values every two seconds. The sensor's event-based API ensures efficient data handling.
ESP-IDF Example
#include "bmp085.h"
#include "esp_log.h"
#define I2C_MASTER_SCL_IO 22
#define I2C_MASTER_SDA_IO 21
#define I2C_MASTER_FREQ_HZ 100000
#define BMP085_ADDR 0x77
static const char *TAG = "BMP085";
void app_main() {
ESP_LOGI(TAG, "Initializing BMP085...");
bmp085_dev dev;
bmp085_init(&dev, I2C_MASTER_SCL_IO, I2C_MASTER_SDA_IO, I2C_MASTER_FREQ_HZ, BMP085_ADDR);
while (1) {
bmp085_data data;
bmp085_read(&dev, &data);
ESP_LOGI(TAG, "Temperature: %.2f°C", data.temperature);
ESP_LOGI(TAG, "Pressure: %.2f hPa", data.pressure);
vTaskDelay(2000 / portTICK_PERIOD_MS);
}
}This ESP-IDF code configures the ESP32 to interface with the BMP085 sensor over I2C. The bmp085_init function initializes the sensor, while the bmp085_read function fetches pressure and temperature readings, which are logged to the console every two seconds.
ESPHome Example
sensor:
- platform: bmp085
temperature:
name: "BMP085 Temperature"
pressure:
name: "BMP085 Pressure"
address: 0x77This ESPHome configuration integrates the BMP085 sensor. It creates sensor entities for temperature and pressure, which are monitored via the I2C address 0x77. The setup is ideal for weather monitoring and IoT systems.
PlatformIO Example
platformio.ini
[env:esp32dev]
platform = espressif32
board = esp32dev
framework = arduino
lib_deps =
adafruit/Adafruit BMP085 Unified Library
wire
monitor_speed = 115200PlatformIO Example Code
#include <Wire.h>
#include "Adafruit_BMP085.h"
Adafruit_BMP085 bmp;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
if (!bmp.begin()) {
Serial.println("Could not find a valid BMP085 sensor, check wiring!");
while (1);
}
}
void loop() {
Serial.print("Temperature: ");
Serial.print(bmp.readTemperature());
Serial.println(" *C");
Serial.print("Pressure: ");
Serial.print(bmp.readPressure() / 100.0);
Serial.println(" hPa");
delay(2000);
}This PlatformIO code integrates the Adafruit BMP085 library to read temperature and pressure values. The data is fetched and printed to the Serial Monitor every two seconds using simple function calls.
MicroPython Example
from machine import I2C, Pin
from bmp085 import BMP085
# Initialize I2C
i2c = I2C(0, scl=Pin(22), sda=Pin(21))
# Initialize BMP085
bmp = BMP085(i2c)
while True:
print(f"Temperature: {bmp.temperature:.2f} °C")
print(f"Pressure: {bmp.pressure / 100:.2f} hPa")
sleep(2)This MicroPython code initializes the BMP085 sensor using I2C. The sensor reads and prints temperature and pressure values to the console every two seconds. It uses the BMP085 MicroPython library for easy integration.
Conclusion
The ESP32 BMP085 Barometric Pressure Sensor is a powerful environment sensor that offers excellent performance and reliability. With support for multiple development platforms including Arduino, ESP-IDF, ESPHome, PlatformIO, and MicroPython, it's a versatile choice for your IoT projects.
For optimal performance, ensure proper wiring and follow the recommended configuration for your chosen development platform.
Always verify power supply requirements and pin connections before powering up your project to avoid potential damage.