ESP32 KY-003 Hall Magnetic Sensor Module
Overview
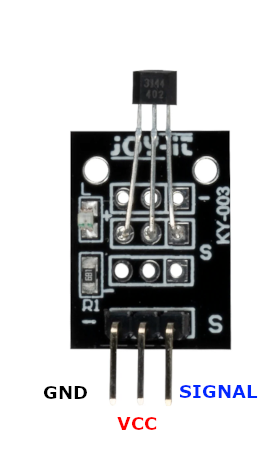
The KY-003 is a Hall Magnetic Sensor Module that detects magnetic fields using the A3144 Hall-effect sensor. It provides a digital output signal when a magnetic field is present, making it suitable for various applications such as proximity sensing and speed detection.
About KY-003 Hall Magnetic Sensor Module
The KY-003 is a Hall-effect sensor module designed to detect magnetic fields using the A3144 Hall-effect sensor. It outputs a digital signal when exposed to a magnetic field, making it ideal for proximity sensing, speed detection, and position tracking in electronic projects.
⚡ Key Features
- Magnetic Field Detection – Activates when a magnet is near the sensor.
- A3144 Hall-Effect Sensor – Provides reliable digital output.
- Simple Interface – Easily integrates with ESP32, Arduino, and other microcontrollers.
- Low Power & Compact Design – Ideal for embedded and battery-powered applications.
- Versatile Applications – Used in speed sensing, position tracking, and magnetic switches.
With its compact design and reliable detection capabilities, the KY-003 is perfect for automation, robotics, and security systems. 🚀
Where to Buy



Prices are subject to change. We earn from qualifying purchases as an Amazon Associate.
Technical Specifications
Pinout Configuration
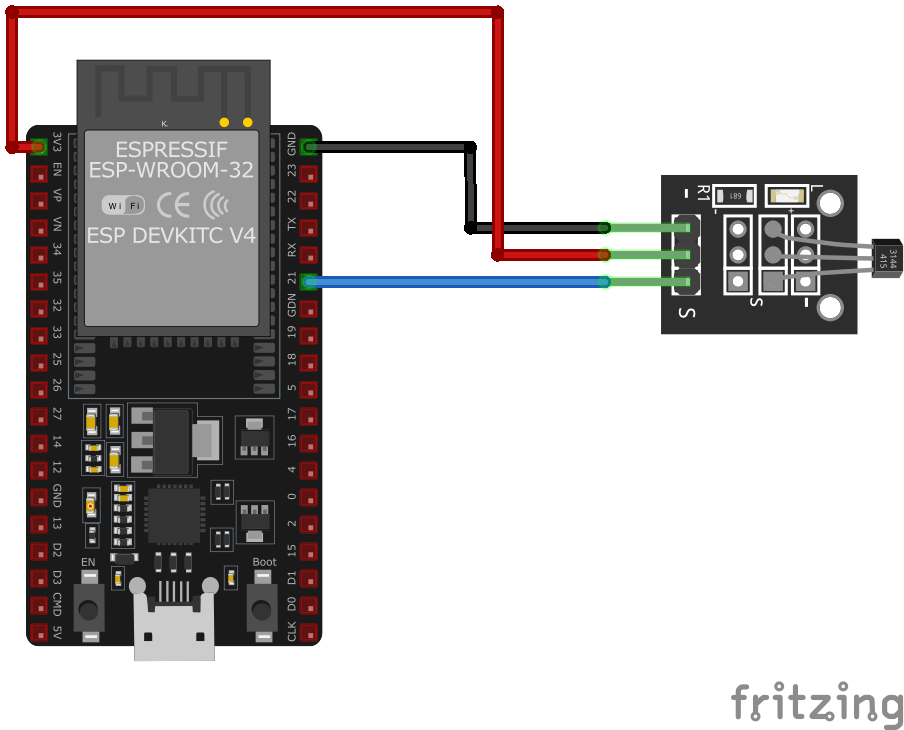
The VCC pin is used to supply power to the sensor, and it typically requires 3.3V or 5V (refer to the datasheet for specific voltage requirements). The GND pin is the ground connection and must be connected to the ground of your ESP32.
Pin (-):Connects to Ground (GND).Pin (+):Connects to VCC (3.3V or 5V).Pin (S):Outputs a digital signal when a magnetic field is detected.
Troubleshooting Guide
Common Issues
❌ No Response from KY-003 Module
Issue: The module does not detect any magnetic fields.
Solutions:
- Verify all connections are secure and correctly placed.
- Ensure the module is receiving the appropriate voltage (3.3V or 5V).
- Check the microcontroller's GPIO pin configuration in the code.
- Test the module with a known magnetic source to confirm functionality.
⚠️ False Triggering of Magnetic Detection
Issue: The module sends signals without any actual magnetic field present.
Solutions:
- Reduce environmental electromagnetic interference that might affect the sensor.
- Implement software debouncing to filter out spurious signals.
- Ensure the module is securely mounted to prevent unintended movements.
Debugging Tips
🔍 Serial Monitor
Use the Serial Monitor to check for error messages and verify the sensor's output. Add debug prints in your code to track the sensor's state.
⚡ Voltage Checks
Use a multimeter to verify voltage levels and check for continuity in your connections. Ensure the power supply is stable and within the sensor's requirements.
Additional Resources
Code Examples
Arduino Example
#define HALL_SENSOR_PIN 7
#define LED_PIN 13
void setup() {
pinMode(HALL_SENSOR_PIN, INPUT);
digitalWrite(HALL_SENSOR_PIN, HIGH); // Enable internal pull-up resistor
pinMode(LED_PIN, OUTPUT);
Serial.begin(9600);
Serial.println("KY-003 Hall Magnetic Sensor Test");
}
void loop() {
int sensorValue = digitalRead(HALL_SENSOR_PIN);
if (sensorValue == LOW) {
Serial.println("Magnetic field detected");
digitalWrite(LED_PIN, HIGH);
} else {
Serial.println("No magnetic field detected");
digitalWrite(LED_PIN, LOW);
}
delay(1000);
}This Arduino code sets up the KY-003 Hall Magnetic Sensor on pin 7 and an LED on pin 13. When a magnetic field is detected, the sensor outputs a LOW signal, triggering the LED to turn on and a message to be printed to the serial monitor.
ESP-IDF Example
#include <stdio.h>
#include "freertos/FreeRTOS.h"
#include "freertos/task.h"
#include "driver/gpio.h"
#define HALL_SENSOR_PIN GPIO_NUM_4
#define LED_PIN GPIO_NUM_2
void app_main(void) {
gpio_set_direction(HALL_SENSOR_PIN, GPIO_MODE_INPUT);
gpio_set_pull_mode(HALL_SENSOR_PIN, GPIO_PULLUP_ONLY);
gpio_set_direction(LED_PIN, GPIO_MODE_OUTPUT);
printf("KY-003 Hall Magnetic Sensor Test\n");
while (1) {
int sensor_value = gpio_get_level(HALL_SENSOR_PIN);
if (sensor_value == 0) {
printf("Magnetic field detected\n");
gpio_set_level(LED_PIN, 1);
} else {
printf("No magnetic field detected\n");
gpio_set_level(LED_PIN, 0);
}
vTaskDelay(pdMS_TO_TICKS(1000));
}
}This ESP-IDF code configures GPIO4 as an input for the KY-003 Hall Magnetic Sensor and GPIO2 as an output for an LED. When a magnetic field is detected (sensor outputs LOW), the LED turns on, and a message is printed to the console.
ESPHome Example
binary_sensor:
- platform: gpio
pin:
number: GPIO4
mode: INPUT_PULLUP
name: "KY-003 Hall Magnetic Sensor"
filters:
- delayed_on: 10ms
- delayed_off: 10ms
on_press:
- then:
- lambda: |-
ESP_LOGD("sensor", "Magnetic field detected!");This ESPHome configuration sets up the KY-003 Hall Magnetic Sensor as a binary sensor on GPIO4 with an internal pull-up resistor. It applies filtering to debounce false triggers and logs when a magnetic field is detected.
PlatformIO Example
platformio.ini
[env:esp32]
platform = espressif32
board = esp32dev
framework = arduinoPlatformIO Example Code
#include <Arduino.h>
#define HALL_SENSOR_PIN 4
#define LED_PIN 2
void setup() {
pinMode(HALL_SENSOR_PIN, INPUT_PULLUP);
pinMode(LED_PIN, OUTPUT);
Serial.begin(115200);
Serial.println("KY-003 Hall Magnetic Sensor Test");
}
void loop() {
if (digitalRead(HALL_SENSOR_PIN) == LOW) {
Serial.println("Magnetic field detected");
digitalWrite(LED_PIN, HIGH);
} else {
Serial.println("No magnetic field detected");
digitalWrite(LED_PIN, LOW);
}
delay(1000);
}This PlatformIO code configures the KY-003 Hall Magnetic Sensor on GPIO4 and an LED on GPIO2. When a magnetic field is detected, the LED turns on, and a message is printed to the serial monitor.
MicroPython Example
import machine
import time
HALL_SENSOR_PIN = machine.Pin(4, machine.Pin.IN, machine.Pin.PULL_UP)
LED_PIN = machine.Pin(2, machine.Pin.OUT)
while True:
if HALL_SENSOR_PIN.value() == 0:
print("Magnetic field detected")
LED_PIN.on()
else:
print("No magnetic field detected")
LED_PIN.off()
time.sleep(1)This MicroPython script configures the KY-003 Hall Magnetic Sensor on GPIO4 and an LED on GPIO2. When a magnetic field is detected (LOW signal), the LED turns on, and a message is printed to the console.
Conclusion
The ESP32 KY-003 Hall Magnetic Sensor Module is a powerful KY-0xx module sensor that offers excellent performance and reliability. With support for multiple development platforms including Arduino, ESP-IDF, ESPHome, PlatformIO, and MicroPython, it's a versatile choice for your IoT projects.
For optimal performance, ensure proper wiring and follow the recommended configuration for your chosen development platform.
Always verify power supply requirements and pin connections before powering up your project to avoid potential damage.