ESP32 KY-022 Infrared Receiver Module
Overview
The KY-022 is an infrared receiver module capable of detecting 38kHz IR signals. It's commonly used in projects requiring remote control signal reception, such as home automation and robotics.
About KY-022 Infrared Receiver Module
The KY-022 Infrared Receiver Module is designed to receive 38kHz modulated infrared signals, commonly used in remote control applications. It can decode signals from various IR remotes, making it ideal for projects involving wireless control. The module operates at voltages between 3.3V and 5V, ensuring compatibility with microcontrollers like Arduino and ESP32. An onboard LED provides visual feedback when an IR signal is detected.
Where to Buy



Prices are subject to change. We earn from qualifying purchases as an Amazon Associate.
Technical Specifications
Pinout Configuration
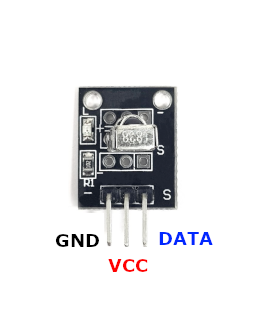
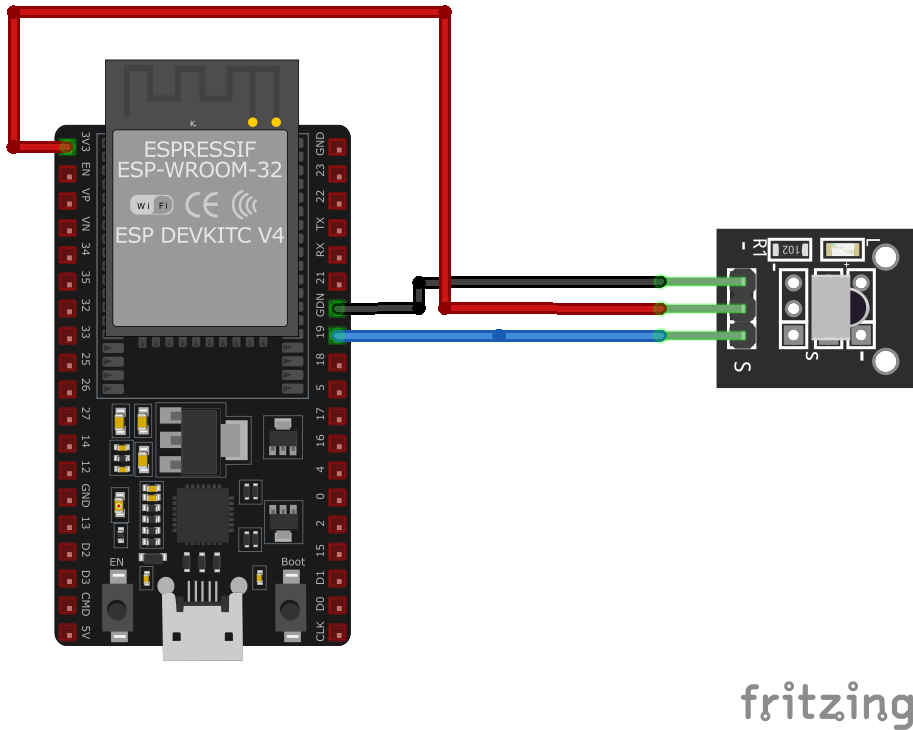
The VCC pin is used to supply power to the sensor, and it typically requires 3.3V or 5V (refer to the datasheet for specific voltage requirements). The GND pin is the ground connection and must be connected to the ground of your ESP32.
Pin (-):Connects to ground (GND).Pin (middle):Connects to VCC (3.3V to 5V).Pin (S):Outputs the demodulated digital signal; connect to a digital input on your microcontroller.
Troubleshooting Guide
Common Issues
❌ No Response from Sensor
Issue: The sensor does not output any signal when an IR remote is used.
Solutions:
- Ensure all connections are secure and correctly placed.
- Verify the module is receiving the appropriate voltage (3.3V to 5V).
- Check if the microcontroller's digital input pin is correctly configured.
- Confirm that the IR remote is functioning and its battery is not depleted.
⚠️ Interference or False Signals
Issue: The sensor outputs signals without any IR input.
Solutions:
- Ensure the module is not exposed to direct sunlight or strong ambient light sources.
- Check for interference from other IR devices in the vicinity.
- Implement software filtering to ignore spurious signals.
Debugging Tips
🔍 Serial Monitor
Use the Serial Monitor to check for error messages and verify the sensor's output. Add debug prints in your code to track the sensor's state.
⚡ Voltage Checks
Use a multimeter to verify voltage levels and check for continuity in your connections. Ensure the power supply is stable and within the sensor's requirements.
Additional Resources
Code Examples
Arduino Example
#include <IRremote.h>
int RECV_PIN = 11; // Define input pin on Arduino
IRrecv irrecv(RECV_PIN);
decode_results results;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
irrecv.enableIRIn(); // Start the receiver
}
void loop() {
if (irrecv.decode(&results)) {
Serial.println(results.value, HEX);
irrecv.resume(); // Receive the next value
}
delay(100); // Small delay to prevent reading errors
}This Arduino code utilizes the IRremote library to receive and decode infrared signals using the KY-022 module. It prints the decoded values to the serial monitor in hexadecimal format.
ESP-IDF Example
#include <stdio.h>
#include "freertos/FreeRTOS.h"
#include "freertos/task.h"
#include "driver/rmt.h"
#include "ir_tools.h"
#define RMT_RX_CHANNEL RMT_CHANNEL_0
#define RMT_RX_GPIO GPIO_NUM_4
#define RMT_CLK_DIV 80
#define RMT_TICK_10_US (80000000 / RMT_CLK_DIV / 100000)
void app_main(void) {
rmt_config_t rmt_rx_config = {
.rmt_mode = RMT_MODE_RX,
.channel = RMT_RX_CHANNEL,
.gpio_num = RMT_RX_GPIO,
.clk_div = RMT_CLK_DIV,
.mem_block_num = 1,
.rx_config = {
.filter_en = true,
.filter_ticks_thresh = 100,
.idle_threshold = RMT_TICK_10_US 1000,
}
};
rmt_config(&rmt_rx_config);
rmt_driver_install(rmt_rx_config.channel, 1000, 0);
ir_parser_config_t ir_parser_config = IR_PARSER_DEFAULT_CONFIG((ir_dev_t)rmt_rx_config.channel);
ir_parser_config.flags |= IR_TOOLS_FLAGS_PROTO_NEC;
ir_parser_handle_t ir_parser = ir_parser_rmt_new_nec(&ir_parser_config);
RingbufHandle_t rb = NULL;
rmt_get_ringbuf_handle(rmt_rx_config.channel, &rb);
rmt_rx_start(rmt_rx_config.channel, true);
printf("KY-022 Infrared Receiver Test\n");
while (1) {
size_t rx_size = 0;
rmt_item32_t items = (rmt_item32_t )xRingbufferReceive(rb, &rx_size, pdMS_TO_TICKS(1000));
if (items) {
ir_nec_data_t nec_data;
if (ir_parser->input(ir_parser, items, rx_size / 4) == ESP_OK) {
if (ir_parser->get_scan_code(ir_parser, &nec_data) == ESP_OK) {
printf("Received NEC code: 0x%08X\n", nec_data);
}
}
vRingbufferReturnItem(rb, (void )items);
}
}
}This ESP-IDF code configures the KY-022 infrared receiver module on GPIO4 using the RMT driver. It continuously listens for NEC protocol IR signals and prints the received data as a hexadecimal value.
ESPHome Example
remote_receiver:
- pin: GPIO4
dump: all
id: ir_receiver
tolerance: 25%
buffer_size: 2kb
filter: 50us
binary_sensor:
- platform: remote_receiver
name: "KY-022 IR Signal Received"
remote_receiver_id: ir_receiverThis ESPHome configuration sets up the KY-022 infrared receiver on GPIO4. It captures all incoming IR signals, stores them in a buffer, and logs received signals. The module can be used with Home Assistant for automation.
PlatformIO Example
platformio.ini
[env:esp32]
platform = espressif32
board = esp32dev
framework = arduino
lib_deps =
z3t0/IRremotePlatformIO Example Code
#include <Arduino.h>
#include <IRremote.h>
#define RECV_PIN 4
IRrecv irrecv(RECV_PIN);
decode_results results;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
irrecv.enableIRIn(); // Start the IR receiver
Serial.println("KY-022 Infrared Receiver Test");
}
void loop() {
if (irrecv.decode(&results)) {
Serial.printf("Received IR Code: 0x%X\n", results.value);
irrecv.resume(); // Receive next value
}
delay(100);
}This PlatformIO code sets up the KY-022 infrared receiver on GPIO4 using the IRremote library. It decodes IR signals and prints the received data as a hexadecimal value.
MicroPython Example
from machine import Pin
import time
IR_PIN = Pin(4, Pin.IN)
def ir_callback(pin):
print("IR signal detected")
IR_PIN.irq(trigger=Pin.IRQ_FALLING, handler=ir_callback)
while True:
time.sleep(1)This MicroPython script configures GPIO4 as an input for the KY-022 infrared receiver. It detects falling edges (IR signals) and prints a message when an IR signal is received.
Conclusion
The ESP32 KY-022 Infrared Receiver Module is a powerful KY-0xx module sensor that offers excellent performance and reliability. With support for multiple development platforms including Arduino, ESP-IDF, ESPHome, PlatformIO, and MicroPython, it's a versatile choice for your IoT projects.
For optimal performance, ensure proper wiring and follow the recommended configuration for your chosen development platform.
Always verify power supply requirements and pin connections before powering up your project to avoid potential damage.