KY-040 Rotary Encoder Module
View on Amazon
Overview
About KY-040 Rotary Encoder Module
The KY-040 Rotary Encoder Module is a rotary input device that provides information about the amount and direction of rotation. Unlike potentiometers, which have limited rotation angles, the KY-040 can rotate continuously, making it ideal for applications requiring precise control, such as volume adjustments, menu navigation, and motor speed control. The module also features a built-in push-button switch, adding an extra layer of functionality.
Get Your KY-040



Prices are subject to change. We earn from qualifying purchases as an Amazon Associate.
KY-040 Specifications
Complete technical specification details for KY-040 Rotary Encoder Module
📊 Technical Parameters
KY-040 Pinout
The **KY-040** is a 5-pin rotary encoder module with integrated push button:
Visual Pinout Diagram
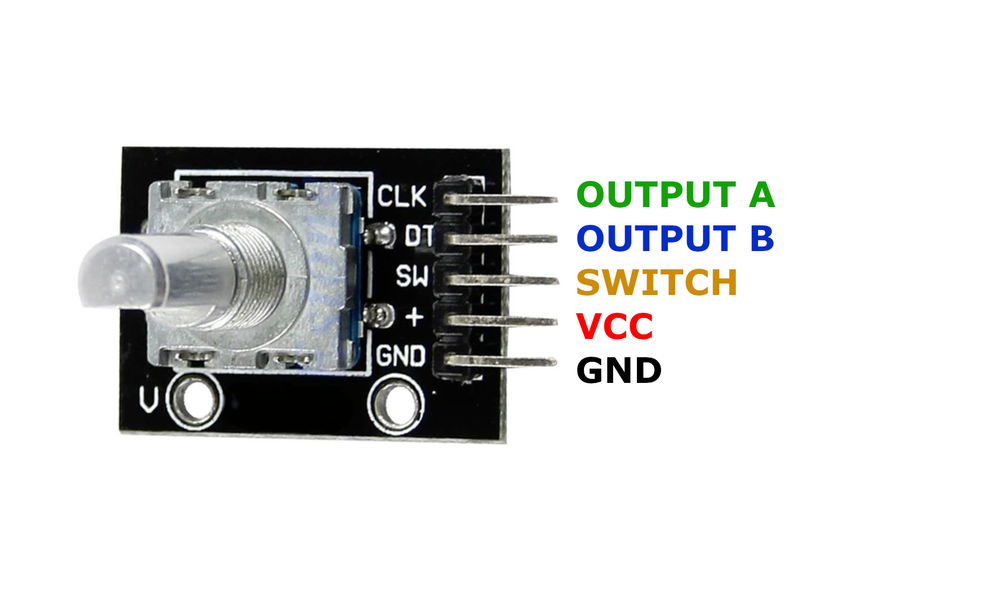
Pin Types
Quick Tips
**Interface**: Digital quadrature encoder (2-phase),🔄 **Rotation**: Continuous 360° rotation (no limits)
**Direction**: CLK and DT phase relationship determines rotation direction,🔘 **Button**: Built-in push-button switch (active low)
**Power**: 3.3V or 5V operation,💡 **Debouncing**: Software debouncing recommended for stable readings
Pin Descriptions
| Pin Name | Type | Description | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
1 CLK | Communication | Clock signal output | Pulses on rotation |
2 DT | Communication | Data signal output | Phase-shifted pulses for direction detection |
3 SW | Control | Switch/button signal | Active low when pressed |
4 VCC | Power | Power supply | 3.3V or 5V |
5 GND | Power | Ground connection |
Wiring KY-040 to ESP32
To interface the **KY-040** with an **ESP32** for rotary input:
Pin Connections
| KY-040 Pin | Connection | ESP32 Pin | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
1 VCC Required | 3.3V | Power supply | |
2 GND Required | GND | Ground | |
3 CLK Required | GPIO18 | Clock input (any GPIO) | |
4 DT Required | GPIO19 | Data input (any GPIO) | |
5 SW Optional | GPIO21 | Button input (any GPIO) |
**Interrupt Pins**: Use interrupt-capable GPIO pins for best response
**GPIO Selection**: Any digital GPIO pins work, shown pins are examples
**Voltage**: Use 3.3V to avoid level shifting
**Software**: Implement debouncing and state machine for direction detection
**Button Optional**: SW pin not required if button functionality not needed
KY-040 Troubleshooting
Common issues and solutions to help you get your sensor working
Common Issues
Issue: The module does not respond or behaves erratically when the knob is rotated.
Solutions:
- Ensure all connections are secure and correctly wired according to the pinout diagram.
- Verify that the microcontroller's input pins are properly configured as inputs in the code.
- Check for proper power supply voltage (3.3V or 5V) to the module.
- Implement software debouncing to account for mechanical switch noise.
Issue: The detected rotation direction is opposite to the actual rotation.
Solutions:
- Swap the connections of the
CLKandDTpins to correct the direction detection. - Ensure that the code logic correctly interprets the sequence of pulses from the
CLKandDTpins.
Debugging Tips
Use the Serial Monitor to check for error messages and verify the sensor's output. Add debug prints in your code to track the sensor's state.
Use a multimeter to verify voltage levels and check for continuity in your connections. Ensure the power supply is stable and within the sensor's requirements.
Additional Resources
KY-040 Programming Examples
Ready-to-use code examples for different platforms and frameworks
#define CLK_PIN 3
#define DT_PIN 4
#define SW_PIN 5
int counter = 0;
int currentStateCLK;
int lastStateCLK;
bool currentStateSW;
bool lastStateSW;
void setup() {
pinMode(CLK_PIN, INPUT);
pinMode(DT_PIN, INPUT);
pinMode(SW_PIN, INPUT_PULLUP);
lastStateCLK = digitalRead(CLK_PIN);
lastStateSW = digitalRead(SW_PIN);
Serial.begin(9600);
Serial.println("KY-040 Rotary Encoder Test");
}
void loop() {
currentStateCLK = digitalRead(CLK_PIN);
if (currentStateCLK != lastStateCLK) {
if (digitalRead(DT_PIN) != currentStateCLK) {
counter++;
} else {
counter--;
}
Serial.print("Position: ");
Serial.println(counter);
}
lastStateCLK = currentStateCLK;
currentStateSW = digitalRead(SW_PIN);
if (currentStateSW == LOW && lastStateSW == HIGH) {
Serial.println("Button Pressed");
}
lastStateSW = currentStateSW;
delay(50);
}This Arduino code sets up the KY-040 rotary encoder using three pins: CLK (Clock), DT (Data), and SW (Switch). It initializes these pins as inputs and continuously monitors the rotation direction and button presses.
When the encoder knob is turned, the CLK and DT pins generate pulses. By comparing the sequence of these pulses, the code determines whether the encoder is rotating clockwise or counterclockwise:
- If the
DTsignal is opposite to theCLKsignal, the counter increments (clockwise rotation). - If the
DTsignal matches theCLKsignal, the counter decrements (counterclockwise rotation).
The position counter is updated accordingly and printed to the serial monitor.
The built-in push-button switch (SW) is also monitored. If pressed, a message is printed to the serial monitor.
A delay(50) is used to debounce the encoder readings, ensuring stable detection of rotation and button presses.
#include <stdio.h>
#include "freertos/FreeRTOS.h"
#include "freertos/task.h"
#include "driver/gpio.h"
#define CLK_PIN GPIO_NUM_18
#define DT_PIN GPIO_NUM_19
#define SW_PIN GPIO_NUM_21
volatile int counter = 0;
volatile int lastStateCLK;
void IRAM_ATTR encoder_isr_handler(void* arg) {
int currentStateCLK = gpio_get_level(CLK_PIN);
if (currentStateCLK != lastStateCLK) {
if (gpio_get_level(DT_PIN) != currentStateCLK) {
counter++;
} else {
counter--;
}
printf("Position: %d\n", counter);
}
lastStateCLK = currentStateCLK;
}
void app_main(void) {
gpio_config_t io_conf = {
.intr_type = GPIO_INTR_ANYEDGE,
.mode = GPIO_MODE_INPUT,
.pin_bit_mask = (1ULL << CLK_PIN) | (1ULL << DT_PIN) | (1ULL << SW_PIN),
.pull_up_en = GPIO_PULLUP_ENABLE
};
gpio_config(&io_conf);
lastStateCLK = gpio_get_level(CLK_PIN);
gpio_install_isr_service(0);
gpio_isr_handler_add(CLK_PIN, encoder_isr_handler, NULL);
printf("KY-040 Rotary Encoder Test\n");
while (1) {
if (gpio_get_level(SW_PIN) == 0) {
printf("Button Pressed\n");
}
vTaskDelay(pdMS_TO_TICKS(100));
}
}This ESP-IDF code configures the KY-040 rotary encoder on GPIO18 (CLK), GPIO19 (DT), and GPIO21 (SW). It uses an interrupt service routine (ISR) to detect changes in the encoder's rotation and update a counter. Additionally, it checks for button presses in the main loop and prints the status to the console.
sensor:
- platform: rotary_encoder
pin_a: GPIO18
pin_b: GPIO19
name: "KY-040 Rotary Encoder"
min_value: -1000
max_value: 1000
resolution: 1
binary_sensor:
- platform: gpio
pin:
number: GPIO21
mode: INPUT_PULLUP
name: "KY-040 Button"This ESPHome configuration sets up the KY-040 rotary encoder with GPIO18 and GPIO19 for rotation detection and GPIO21 for the push button. The encoder is configured with a minimum and maximum value range, and its resolution is set to 1 step per increment.
platformio.ini
[env:esp32]
platform = espressif32
board = esp32dev
framework = arduinomain.cpp
#include <Arduino.h>
#define CLK_PIN 18
#define DT_PIN 19
#define SW_PIN 21
volatile int counter = 0;
int lastStateCLK;
void IRAM_ATTR rotary_encoder() {
int currentStateCLK = digitalRead(CLK_PIN);
if (currentStateCLK != lastStateCLK) {
if (digitalRead(DT_PIN) != currentStateCLK) {
counter++;
} else {
counter--;
}
Serial.print("Position: ");
Serial.println(counter);
}
lastStateCLK = currentStateCLK;
}
void setup() {
pinMode(CLK_PIN, INPUT);
pinMode(DT_PIN, INPUT);
pinMode(SW_PIN, INPUT_PULLUP);
attachInterrupt(digitalPinToInterrupt(CLK_PIN), rotary_encoder, CHANGE);
Serial.begin(115200);
Serial.println("KY-040 Rotary Encoder Test");
}
void loop() {
if (digitalRead(SW_PIN) == LOW) {
Serial.println("Button Pressed");
delay(100);
}
}This PlatformIO code configures GPIO18 (CLK), GPIO19 (DT), and GPIO21 (SW) for the KY-040 rotary encoder. It uses an interrupt to detect changes in rotation and updates a counter accordingly. The push button state is also monitored and printed to the serial monitor when pressed.
import machine
import time
CLK_PIN = machine.Pin(18, machine.Pin.IN, machine.Pin.PULL_UP)
DT_PIN = machine.Pin(19, machine.Pin.IN, machine.Pin.PULL_UP)
SW_PIN = machine.Pin(21, machine.Pin.IN, machine.Pin.PULL_UP)
counter = 0
last_state_clk = CLK_PIN.value()
while True:
current_state_clk = CLK_PIN.value()
if current_state_clk != last_state_clk:
if DT_PIN.value() != current_state_clk:
counter += 1
else:
counter -= 1
print("Position:", counter)
last_state_clk = current_state_clk
if SW_PIN.value() == 0:
print("Button Pressed")
time.sleep(0.1)
time.sleep(0.05)This MicroPython script configures GPIO18 (CLK), GPIO19 (DT), and GPIO21 (SW) for the KY-040 rotary encoder. It continuously monitors the encoder rotation and updates a counter while also detecting button presses.
Wrapping Up KY-040
The ESP32 KY-040 Rotary Encoder Module is a powerful KY-0xx module sensor that offers excellent performance and reliability. With support for multiple development platforms including Arduino, ESP-IDF, ESPHome, PlatformIO, and MicroPython, it's a versatile choice for your IoT projects.
Best Practices
For optimal performance, ensure proper wiring and follow the recommended configuration for your chosen development platform.
Safety First
Always verify power supply requirements and pin connections before powering up your project to avoid potential damage.
Ready to Start Building?
Now that you have all the information you need, it's time to integrate the KY-040 into your ESP32 project and bring your ideas to life!
Explore Alternative Sensors
Looking for alternatives to the KY-040? Check out these similar sensors that might fit your project needs.
The KY-021 is a mini magnetic reed switch module that detects the presence of a magnetic field. It provides a digital signal output, making...
The KY-004 is a key switch module equipped with a tactile push-button. It provides a digital output signal when pressed, making it ideal for...