RC522 RFID/NFC Module
View on Amazon
Overview
About RC522 RFID/NFC Module
The RC522 is a cost-effective and compact RFID/NFC module designed for proximity identification and security applications. It supports multiple communication protocols (SPI, I²C, UART), making it easy to integrate with ESP32, Arduino, and other microcontrollers.
⚡ Key Features
- Multi-Protocol Support – Communicates via SPI, I²C, and UART.
- ISO/IEC 14443 Type A Compatibility – Works with RFID/NFC cards and tags.
- Versatile Applications – Ideal for access control, payment systems, and secure authentication.
- Compact & Low Power – Suitable for embedded security projects.
With its flexibility and affordability, the RC522 is a great choice for NFC-based applications requiring secure and contactless authentication. 🚀
Get Your RC522



Prices are subject to change. We earn from qualifying purchases as an Amazon Associate.
RC522 Specifications
Complete technical specification details for RC522 RFID/NFC Module
📊 Technical Parameters
RC522 Pinout
The RC522 supports multiple communication protocols (SPI, I²C, UART) with 8 main pins for interfacing.
Visual Pinout Diagram
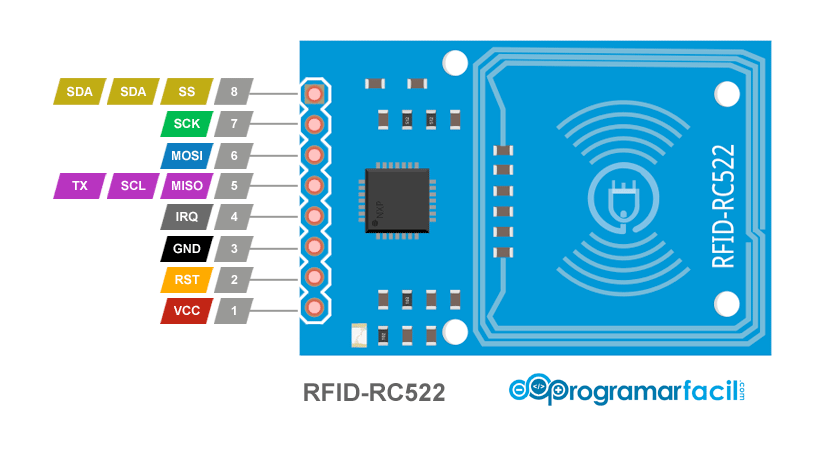
Pin Types
Quick Tips
ISO/IEC 14443 Type A RFID/NFC tags (13.56 MHz),[object Object]
Object],[object Object]
is the most widely used interface for RC522
Pin Descriptions
| Pin Name | Type | Description | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
1 VCC | Power | Power supply input (3.3V). Typically 3.3V for most modules. | Some modules support 5V - check your specific module. |
2 GND | Power | Ground connection. Connect to system ground. | |
3 RST | Control | Reset signal (active low). Used to reset the module. | Connect to GPIO for software reset control. |
4 IRQ | Interrupt | Interrupt signal output. Triggers when card is detected. | Optional - can be left unconnected for polling mode. |
5 MISO | SPI | SPI Master In Slave Out. Data from RC522 to microcontroller. | Connect to ESP32 MISO (GPIO 19). |
6 MOSI | SPI | SPI Master Out Slave In. Data from microcontroller to RC522. | Connect to ESP32 MOSI (GPIO 23). |
7 SCK | SPI | SPI clock line. Clock signal for SPI communication. | Connect to ESP32 SCK (GPIO 18). |
8 SDA/SS | SPI/I2C | SPI: Slave Select (chip select). I²C: Serial Data line. | For SPI: Connect to any GPIO (e.g., GPIO 5). For I²C: data line. |
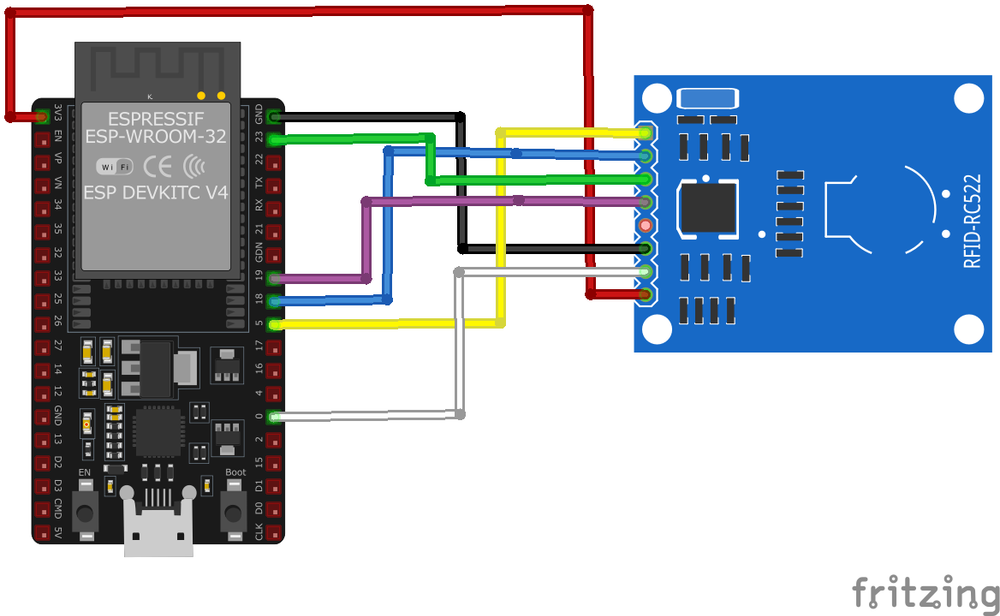
Wiring RC522 to ESP32
To interface the RC522 with an ESP32 via SPI, connect VCC to 3.3V, GND to ground, and the SPI pins (MISO, MOSI, SCK, SDA/SS) to the corresponding ESP32 SPI pins.
Visual Wiring Diagram
Connection Status
Protocol
Pin Connections
| RC522 Pin | Connection | ESP32 Pin | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
1 VCC Required | 3.3V | Power supply. Use 3.3V for most modules. | |
2 GND Required | GND | Ground connection. | |
3 RST Required | GPIO 4 | Reset control. Any available GPIO pin. | |
4 MISO Required | GPIO 19 | SPI MISO - data from RC522 to ESP32. | |
5 MOSI Required | GPIO 23 | SPI MOSI - data from ESP32 to RC522. | |
6 SCK Required | GPIO 18 | SPI clock signal. | |
7 SDA/SS Required | GPIO 5 | SPI Slave Select (chip select). Any available GPIO. | |
8 IRQ Optional | Optional GPIO | Interrupt pin for card detection (optional). |
is the recommended interface (most reliable and well-documented)
MFRC522 library for Arduino/ESP32 compatibility
Object]
Object]
Object]
pin optional - polling mode works fine for most applications
antenna parallel to RFID tag for best reading performance
100µF capacitor across VCC and GND for stable operation
RC522 Troubleshooting
Common issues and solutions to help you get your sensor working
Common Issues
Issue: The RC522 module does not power up or respond to commands.
Possible causes include insufficient power supply, incorrect wiring, or faulty hardware.
Solution: Ensure the module is connected to a stable power source within the recommended voltage range of 3.3V to 5V. Verify that all connections are secure and correctly configured. If the problem persists, consider testing the module with a different power source or replacing it.
Issue: The module fails to communicate with the microcontroller over the chosen interface (SPI).
Possible causes include incorrect wiring, improper interface selection, or incompatible voltage levels.
Solution: Double-check the wiring to ensure correct connections for SPI communication. For SPI, verify the MOSI, MISO, SCK, and SS lines are properly connected. Ensure that the microcontroller's SPI interface is enabled and configured correctly.
Issue: The module initializes correctly but fails to read RFID tags.
Possible causes include incorrect antenna orientation, insufficient power supply, or interference from nearby electronic devices.
Solution: Ensure the module's antenna is properly oriented and positioned near the tags. Verify that the power supply provides adequate current for the module's operation. Keep the module away from sources of electromagnetic interference.
Issue: The module detects tags intermittently or with delays.
Possible causes include low-quality tags, environmental interference, or firmware issues.
Solution: Test with different tags to rule out tag quality issues. Ensure the operating environment is free from strong electromagnetic interference. Update the module's firmware to the latest version to benefit from bug fixes and improvements.
Issue: The module operates erratically or produces errors during operation.
Possible causes include outdated or incompatible libraries, incorrect initialization, or software bugs.
Solution: Ensure that the latest version of the MFRC522 library is installed and compatible with your development environment. Review the initialization code to confirm that the module is set up correctly. Consult the module's documentation and community forums for guidance on proper usage.
Debugging Tips
Use the Serial Monitor to check for error messages and verify the sensor's output. Add debug prints in your code to track the sensor's state.
Use a multimeter to verify voltage levels and check for continuity in your connections. Ensure the power supply is stable and within the sensor's requirements.
Additional Resources
RC522 Programming Examples
Ready-to-use code examples for different platforms and frameworks
#include <SPI.h>
#include <MFRC522.h>
#define RST_PIN 9
#define SS_PIN 10
MFRC522 rfid(SS_PIN, RST_PIN);
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
SPI.begin();
rfid.PCD_Init();
Serial.println("RC522 initialized. Waiting for cards...");
}
void loop() {
if (!rfid.PICC_IsNewCardPresent() || !rfid.PICC_ReadCardSerial()) {
delay(50);
return;
}
Serial.print("Card UID: ");
for (byte i = 0; i < rfid.uid.size; i++) {
Serial.print(rfid.uid.uidByte[i], HEX);
Serial.print(" ");
}
Serial.println();
rfid.PICC_HaltA();
}#include <stdio.h>
#include "driver/spi_master.h"
#include "driver/gpio.h"
#include "freertos/task.h"
#include "rc522.h"
#define RST_PIN GPIO_NUM_21
#define SS_PIN GPIO_NUM_22
#define MISO_PIN GPIO_NUM_19
#define MOSI_PIN GPIO_NUM_23
#define SCK_PIN GPIO_NUM_18
void app_main() {
printf("Initializing RC522...");
rc522_config_t config = {
.spi_miso_io = MISO_PIN,
.spi_mosi_io = MOSI_PIN,
.spi_sck_io = SCK_PIN,
.spi_cs_io = SS_PIN,
.reset_io = RST_PIN
};
rc522_handle_t handle = rc522_create(&config);
if (handle == NULL) {
printf("Failed to initialize RC522\n");
return;
}
while (true) {
rc522_tag_t tag;
if (rc522_read_tag(handle, &tag) == ESP_OK) {
printf("Tag UID: ");
for (int i = 0; i < tag.uid_size; i++) {
printf("%02X ", tag.uid[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
vTaskDelay(pdMS_TO_TICKS(500));
}
}spi:
clk_pin: GPIO18
mosi_pin: GPIO23
miso_pin: GPIO19
rc522:
cs_pin: GPIO22
rst_pin: GPIO21
update_interval: 2s
sensor:
- platform: rc522
uid:
name: "RFID Tag UID"
log:
name: "RFID Log"platformio.ini
[env:rc522]
platform = espressif32
board = esp32dev
framework = arduino
monitor_speed = 115200main.cpp
#include <SPI.h>
#include <MFRC522.h>
#define RST_PIN 21
#define SS_PIN 22
MFRC522 rfid(SS_PIN, RST_PIN);
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
SPI.begin();
rfid.PCD_Init();
Serial.println("RC522 initialized. Waiting for cards...");
}
void loop() {
if (!rfid.PICC_IsNewCardPresent() || !rfid.PICC_ReadCardSerial()) {
delay(50);
return;
}
Serial.print("Card UID: ");
for (byte i = 0; i < rfid.uid.size; i++) {
Serial.print(rfid.uid.uidByte[i], HEX);
Serial.print(" ");
}
Serial.println();
rfid.PICC_HaltA();
}from machine import Pin, SPI
from mfrc522 import MFRC522
import time
spi = SPI(1, baudrate=1000000, sck=Pin(18), mosi=Pin(23), miso=Pin(19))
rst = Pin(21, Pin.OUT)
cs = Pin(22, Pin.OUT)
reader = MFRC522(spi, cs, rst)
while True:
print("Waiting for card...")
(status, tag_type) = reader.request(reader.REQIDL)
if status == reader.OK:
(status, uid) = reader.anticoll()
if status == reader.OK:
print("Card UID:", [hex(i) for i in uid])
time.sleep(1)Wrapping Up RC522
The ESP32 RC522 RFID/NFC Module is a powerful NFC sensor that offers excellent performance and reliability. With support for multiple development platforms including Arduino, ESP-IDF, ESPHome, PlatformIO, and MicroPython, it's a versatile choice for your IoT projects.
Best Practices
For optimal performance, ensure proper wiring and follow the recommended configuration for your chosen development platform.
Safety First
Always verify power supply requirements and pin connections before powering up your project to avoid potential damage.
Ready to Start Building?
Now that you have all the information you need, it's time to integrate the RC522 into your ESP32 project and bring your ideas to life!
Explore Alternative Sensors
Looking for alternatives to the RC522? Check out these similar sensors that might fit your project needs.