ESP32 SHT31 / SHT31-D / GY-SHT31 / SI7021 Temperature and Humidity Sensor Pinout
Overview
The SHT31 series sensors utilize Sensirion's CMOSens® technology to deliver accurate, stable, and linear temperature and humidity data. Their robust calibration and long-term reliability make them ideal for applications that require consistent performance under varying conditions.
About SHT31 / SHT31-D / GY-SHT31 / SI7021 Temperature and Humidity Sensor
The SHT31, SHT31-D, GY-SHT31, and SI7021 sensors share a similar architecture, delivering high-accuracy temperature and humidity measurements. An improvement over the SHT30, the SHT31 series offers enhanced reliability and performance, making it ideal for HVAC systems, environmental monitoring, data logging, and IoT applications.
⚡ Key Features
- Improved Accuracy & Stability – More precise than previous models.
- I²C Communication – Seamless integration with ESP32, Arduino, and microcontrollers.
- Enhanced Performance – Faster response time and better long-term reliability.
- Versatile Applications – Used in industrial, smart home, and scientific monitoring systems.
With its higher precision and durability, the SHT31 series is a great choice for demanding climate monitoring applications. 🚀
For applications demanding even higher precision, faster response times, or specialized features, consider the SHT35 sensor, which provides superior performance for demanding environments.
Where to Buy SHT31 / SHT31-D / GY-SHT31 / SI7021 Temperature and Humidity Sensor



Prices are subject to change. We earn from qualifying purchases as an Amazon Associate.
SHT31 / SHT31-D / GY-SHT31 / SI7021 Datasheet and Technical Specifications
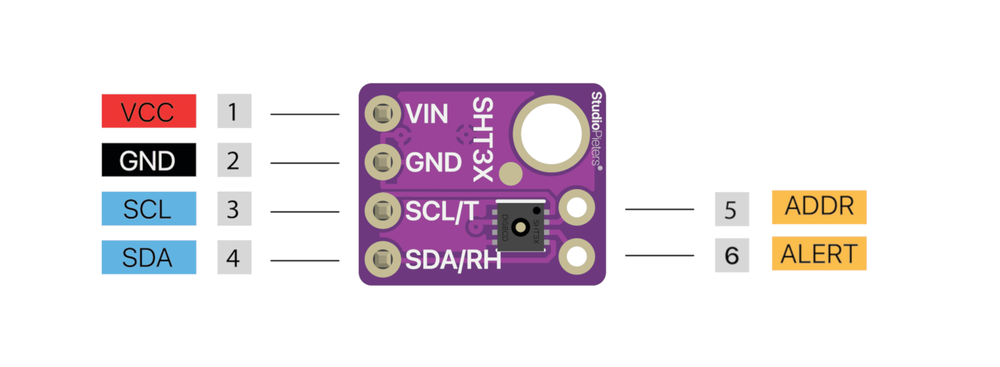
SHT31 / SHT31-D / GY-SHT31 / SI7021 Pinout Diagram
The VCC pin is used to supply power to the sensor, and it typically requires 3.3V or 5V (refer to the datasheet for specific voltage requirements). The GND pin is the ground connection and must be connected to the ground of your ESP32.
The SHT31 pinout is as follows:
- VDD: Power supply voltage (2.15V to 5.5V).
- GND: Ground.
- SDA: Serial Data Line for I2C communication.
- SCL: Serial Clock Line for I2C communication.
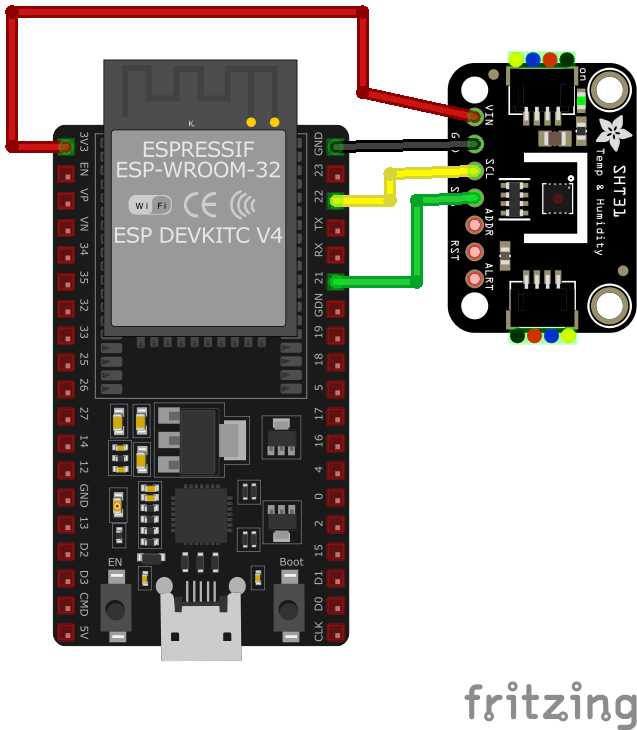
SHT31 / SHT31-D / GY-SHT31 / SI7021 Wiring with ESP32
- Connect VDD to the 3.3V pin on the ESP32.
- Connect GND to the ground (GND) of the ESP32.
- Connect SDA to the ESP32's GPIO21 (default I2C data pin).
- Connect SCL to the ESP32's GPIO22 (default I2C clock pin).
- Place pull-up resistors (10kΩ) between SDA and VDD, and SCL and VDD, to ensure reliable communication.
SHT31 / SHT31-D / GY-SHT31 / SI7021 Troubleshooting Guide
Common Issues
⏸️ Sensor Stops Working After a Minute
Issue: The SHT31-D sensor functions correctly for a few minutes but then ceases to provide readings. The serial monitor may display repeated messages such as Failed to read temperature and Failed to read humidity.
Possible causes include unstable connections, power supply issues, or sensor malfunction.
Solution: Ensure all connections are secure and that the sensor is receiving a stable power supply. Consider testing with different wires or a breadboard to rule out connection issues. If the problem persists, the sensor may need to be power-cycled or replaced.
❄️ Incorrect Negative Temperature Readings
Issue: When measuring negative temperatures, the SHT31 sensor returns incorrect values, such as 42949672.0°C, instead of the expected negative readings.
Possible causes include limitations of the specific sensor model or issues with the data conversion method used in the code.
Solution: Verify that the sensor model supports the desired temperature range. If the sensor is appropriate, review the data conversion logic in the code to ensure it correctly handles negative values.
💻 Compilation Error: 'Wire1' Not Declared
Issue: Attempting to compile code results in the error message: 'Wire1' was not declared in this scope.
Possible causes include the use of code intended for a different microcontroller that supports multiple I2C interfaces, while the current microcontroller does not.
Solution: Modify the code to use the appropriate I2C interface for your microcontroller. For instance, replace instances of Wire1 with Wire if only one I2C interface is available.
❌ Sensor Not Detected at Expected I2C Address
Issue: The SHT31 sensor is not detected at the expected I2C address 0x44 or 0x45, leading to communication failures.
Possible causes include incorrect wiring of the address pin or improper sensor initialization.
Solution: Verify the connection of the address pin (ADDR) to set the desired I2C address: connecting to GND sets the address to 0x44, while connecting to VCC sets it to 0x45. Ensure the code matches the configured address and that the sensor is properly initialized.
Debugging Tips
🔍 Serial Monitor
Use the Serial Monitor to check for error messages and verify the sensor's output. Add debug prints in your code to track the sensor's state.
⚡ Voltage Checks
Use a multimeter to verify voltage levels and check for continuity in your connections. Ensure the power supply is stable and within the sensor's requirements.
Additional Resources
SHT31 / SHT31-D / GY-SHT31 / SI7021 Code Examples
Arduino Example
#include <Wire.h>
#include "Adafruit_SHT31.h"
Adafruit_SHT31 sht31 = Adafruit_SHT31();
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
while (!Serial) delay(10);
if (!sht31.begin(0x44)) { // Set to 0x45 for alternate I2C address
Serial.println("Couldn't find SHT31");
while (1) delay(1);
}
}
void loop() {
float t = sht31.readTemperature();
float h = sht31.readHumidity();
if (!isnan(t) && !isnan(h)) { // Check if readings are valid
Serial.print("Temp *C = "); Serial.print(t); Serial.print(" ");
Serial.print("Hum. % = "); Serial.println(h);
} else {
Serial.println("Failed to read from SHT31 sensor");
}
delay(1000);
}ESP-IDF Example
#include <stdio.h>
#include "freertos/FreeRTOS.h"
#include "freertos/task.h"
#include "driver/i2c.h"
#define I2C_MASTER_SCL_IO 22 /!< GPIO number used for I2C master clock /
#define I2C_MASTER_SDA_IO 21 /!< GPIO number used for I2C master data /
#define I2C_MASTER_NUM I2C_NUM_0 /!< I2C master I2C port number /
#define I2C_MASTER_FREQ_HZ 100000 /!< I2C master clock frequency /
#define SHT31_SENSOR_ADDR 0x44 /!< SHT31 I2C address /
static esp_err_t i2c_master_init(void) {
i2c_config_t conf = {
.mode = I2C_MODE_MASTER,
.sda_io_num = I2C_MASTER_SDA_IO,
.scl_io_num = I2C_MASTER_SCL_IO,
.sda_pullup_en = GPIO_PULLUP_ENABLE,
.scl_pullup_en = GPIO_PULLUP_ENABLE,
.master.clk_speed = I2C_MASTER_FREQ_HZ,
};
esp_err_t err = i2c_param_config(I2C_MASTER_NUM, &conf);
if (err != ESP_OK) {
return err;
}
return i2c_driver_install(I2C_MASTER_NUM, conf.mode, 0, 0, 0);
}
void read_sht31_sensor() {
uint8_t data[6];
i2c_master_write_read_device(I2C_MASTER_NUM, SHT31_SENSOR_ADDR, NULL, 0, data, sizeof(data), pdMS_TO_TICKS(1000));
uint16_t temp_raw = (data[0] << 8) | data[1];
uint16_t hum_raw = (data[3] << 8) | data[4];
float temperature = -45 + 175 ((float)temp_raw / 65535.0);
float humidity = 100 ((float)hum_raw / 65535.0);
printf("Temperature: %.2f °C, Humidity: %.2f %%\n", temperature, humidity);
}
void app_main() {
ESP_ERROR_CHECK(i2c_master_init());
while (1) {
read_sht31_sensor();
vTaskDelay(pdMS_TO_TICKS(2000));
}
}ESPHome Example
sensor:
- platform: sht3x
address: 0x44
temperature:
name: "Room Temperature"
humidity:
name: "Room Humidity"
update_interval: 60ssht3x platform to integrate SHT31 sensors. It reads and updates temperature and humidity values every 60 seconds, with descriptive names like 'Room Temperature' and 'Room Humidity.'PlatformIO Example
platformio.ini
[env:esp32dev]
platform = espressif32
board = esp32dev
framework = arduino
lib_deps =
adafruit/Adafruit SHT31 Library @ ^2.0.0
monitor_speed = 115200PlatformIO Example Code
#include <Wire.h>
#include "Adafruit_SHT31.h"
Adafruit_SHT31 sht31 = Adafruit_SHT31();
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
while (!Serial) delay(10);
if (!sht31.begin(0x44)) { // Default I2C address for SHT31
Serial.println("Couldn't find SHT31 sensor!");
while (1) delay(1);
}
}
void loop() {
float temperature = sht31.readTemperature();
float humidity = sht31.readHumidity();
if (!isnan(temperature) && !isnan(humidity)) {
Serial.print("Temperature: ");
Serial.print(temperature);
Serial.println(" °C");
Serial.print("Humidity: ");
Serial.print(humidity);
Serial.println(" %");
} else {
Serial.println("Failed to read from SHT31 sensor");
}
delay(2000);
}MicroPython Example
from machine import I2C, Pin
from time import sleep
import sht31
# Initialize I2C interface
i2c = I2C(0, scl=Pin(22), sda=Pin(21))
# Initialize the SHT31 sensor
sensor = sht31.SHT31(i2c, addr=0x44)
print("SHT31 Sensor Example")
while True:
try:
temperature, humidity = sensor.measure()
print("Temperature: {:.2f} °C".format(temperature))
print("Humidity: {:.2f} %".format(humidity))
except Exception as e:
print("Error reading from SHT31: ", e)
sleep(2)Conclusion
The ESP32 SHT31 / SHT31-D / GY-SHT31 / SI7021 Temperature and Humidity Sensor is a powerful environment sensor that offers excellent performance and reliability. With support for multiple development platforms including Arduino, ESP-IDF, ESPHome, PlatformIO, and MicroPython, it's a versatile choice for your IoT projects.
For optimal performance, ensure proper wiring and follow the recommended configuration for your chosen development platform.
Always verify power supply requirements and pin connections before powering up your project to avoid potential damage.