ESP32-S3 Super Mini is a development board based on the ESP32S3 microcontroller using XTENSA architecture.
This board features a maximum CPU frequency of 240 MHz and 4MB flash memory.
About ESP32-S3 Super Mini
🚀 The ESP32-S3 SuperMini is a compact and powerful IoT development board based on the Espressif ESP32-S3 WiFi/Bluetooth dual-mode chip. Featuring a dual-core Xtensa LX7 processor running up to 240 MHz, it delivers impressive performance for your embedded projects. ⚡
📡 For seamless wireless connectivity, it supports WiFi 802.11b/g/n and Bluetooth 5 (LE), making it ideal for IoT applications. Just like the ESP32-C3 SuperMini, this board includes a built-in PCB antenna, ensuring reliable signal strength without requiring an external antenna.
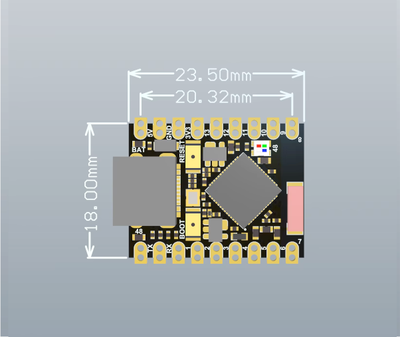
💾 Equipped with 512 KB SRAM and 4 MB flash memory, there's plenty of space for your firmware and applications. Its ultra-compact design (22.52 x 18 mm) makes it easy to embed into small projects
🆚 Wondering how the ESP32-S3 SuperMini compares to other SuperMini boards? Check out our full comparison guide to see how it stacks up against the C3, C3 Plus, C6, and H2.
Where to Buy ESP32-S3 Super Mini
Prices are subject to change. We earn from qualifying purchases as an Amazon Associate.
📋 Technical Specifications
Complete technical specification details for ESP32-S3 Super Mini
🔌 USB
🛰️ Connectivity
🧠 Microcontroller
✨ Features & Pins
- • Ultra-small size: 22.52 x 18 mm
- • Ultra-low power consumption: deep sleep power consumption of about 43μA
- • Onboard WS2812 RGB LED for programmable multi-color status indication
- • Dual-core Xtensa LX7 CPU running at up to 240 MHz
- • 512 KB SRAM, 384 KB ROM built-in, with 4 MB Flash
- • Secure encryption features: AES-128/256, RSA, HMAC, digital signatures, and secure startup
ESP32-S3 Super Mini Board Dimensions
Physical measurements for ESP32-S3 Super Mini
3D Printed Cases
Professional enclosures for ESP32-S3 Super Mini
Features:
ESP32-S3 Super Mini Pinout Diagram
Complete pin reference for ESP32-S3 Super Mini
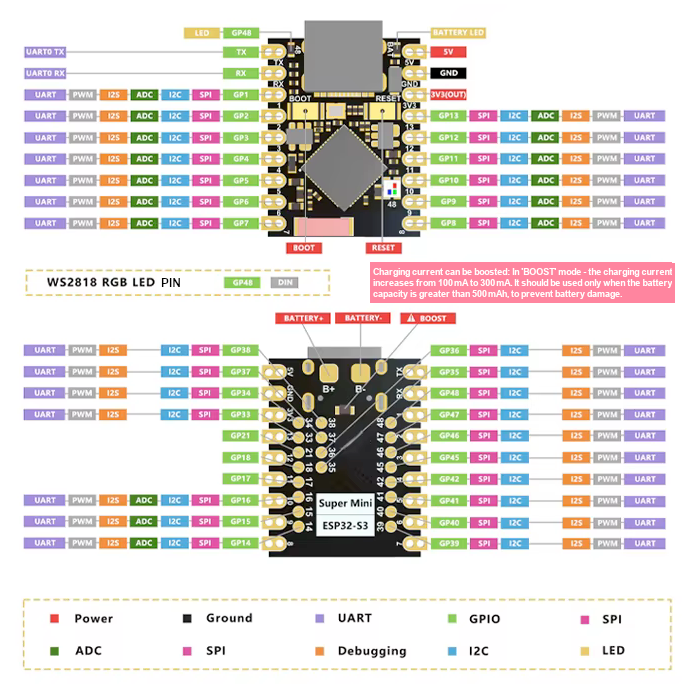
The ESP32-S3 Super Mini pinout is designed for maximum functionality in a compact package. The board provides essential power pins like 5V, 3.3V, and GND for stable power delivery.
It includes communication interfaces such as RX and TX for UART, SDA and SCL for I2C, and MISO, MOSI, SCK, and SS for SPI, ensuring seamless integration with peripherals.
For analog input, the ESP32-S3 Super Mini offers ADC pins labeled A0 to A5, making it suitable for sensor data acquisition. Additionally, it features an onboard WS2812 RGB LED, which allows programmable multi-color status indications for enhanced user feedback.
✅ Safe Pins to Use
These pins are safe for general GPIO usage without boot or system conflicts
💡 Why Are These Pins Safe?
⚠️ Pins to Avoid or Use with Caution
Reserved for critical functions. Misuse may cause boot failures, programming issues, or system conflicts.
Boot behavior & flash voltage
Low-level debugging interface
USB Serial/JTAG communication
Memory & PSRAM connections
Debugging & firmware uploads
| PIN | Label | Why Avoid | Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| IO3 | GPIO3 | Sampled at reset to select JTAG interface (USB Serial/JTAG controller vs. external pins). Improper use can disable external JTAG or alter debug interface. | 🛠️ Strapping |
| IO9 | FSPIHD | Connected to external flash (data/hold signal) on most modules. Not recommended for use as GPIO, since it must remain dedicated to flash communication. | ⚡ Flash |
| IO10 | FSPICS0 | Used to select the external flash chip. It is required for flash access and cannot be repurposed without losing flash connectivity | ⚡ Flash |
| IO11 | FSPID | Used as a data line for flash (and in-package PSRAM). It should not be used as GPIO when the flash/PSRAM is in use. | ⚡ Flash |
| IO12 | FSPICLK | Drives the flash (and PSRAM) clock. This critical signal must be reserved for memory and not used as general GPIO. | ⚡ Flash |
| IO13 | FSPIQ | Used as a data line for flash/PSRAM transfers. Not available for other uses when flash/PSRAM is connected. | ⚡ Flash |
| IO14 | FSPIWP | Connected to external flash (data/write-protect signal). Not recommended as GPIO because it’s reserved for flash operations. | ⚡ Flash |
| IO33 | FSPIHD | On chips/modules with integrated flash, this IO is wired to the flash hold pin internally. It cannot be reassigned to GPIO without breaking flash access. | ⚡ Flash |
| IO34 | FSPICS0 | Wired to the chip select of the internal flash in flash-equipped variants. It must remain low during flash operation, so it’s not available for other use. | ⚡ Flash |
| IO35 | FSPID / PSRAM_D0 | In modules with octal PSRAM, this pin is connected to the PSRAM data line. It is reserved for memory interface and not free for general GPIO when flash/PSRAM is present. | ⚡ Flash |
| IO36 | FSPICLK / PSRAM_CLK | In modules with octal PSRAM, this pin drives the PSRAM clock. It must be dedicated to the memory interface, not used as a regular GPIO when that interface is in use. | ⚡ Flash |
| IO37 | FSPIQ / PSRAM_DQS | In modules with octal PSRAM, this pin is connected to the PSRAM’s DQS signal. It cannot be repurposed without disrupting the PSRAM/flash communication. | ⚡ Flash |
| IO38 | FSPIWP | On flash-equipped chips, this pin is tied to the flash’s WP# (or D3) line. It should be avoided for other use, as it’s needed for flash operations. | ⚡ Flash |
| IO39 | MTCK (GPIO39) | Default JTAG debugging TCK pin. If JTAG is needed, this pin must be free; it may also be used internally for PSRAM chip select on certain modules, so avoid repurposing it. | 🪛 Other |
| IO40 | MTDO (GPIO40) | Default JTAG TDO output for debugging. Using it as GPIO will interfere with JTAG debugging functionality. | 🪛 Other |
| IO41 | MTDI (GPIO41) | Default JTAG TDI input for debugging. Should be reserved for JTAG or left unused if JTAG is to remain available. | 🪛 Other |
| IO45 | GPIO45 | Determines flash/PSRAM power voltage (3.3 V vs 1.8 V) at boot. Must match hardware configuration; using as GPIO can upset flash supply setting. | 🛠️ Strapping |
| IO46 | GPIO46 | Must be at a defined level during reset (with GPIO0) to select normal or download boot and UART/USB print mode. This pin is input-only (no output drive), so it should be left for its intended strapping function. | 🛠️ Strapping |
| IO47 | SPICLK_P | Used only on variants with Octal SPI interface (e.g. ESP32-S3R16V) as part of the differential clock pair. On such chips it operates at 1.8 V and is reserved for the high-speed octal SPI clock, not for general GPIO use. | ⚡ Flash |
| IO48 | SPICLK_N | Used only on variants with Octal SPI interface, as the negative leg of the differential clock&. On such chips it operates at 1.8 V; it should be avoided for GPIO to prevent conflicts with the octal flash/PSRAM clock. | ⚡ Flash |
On-Board LEDs
LED indicators on ESP32-S3 Super Mini
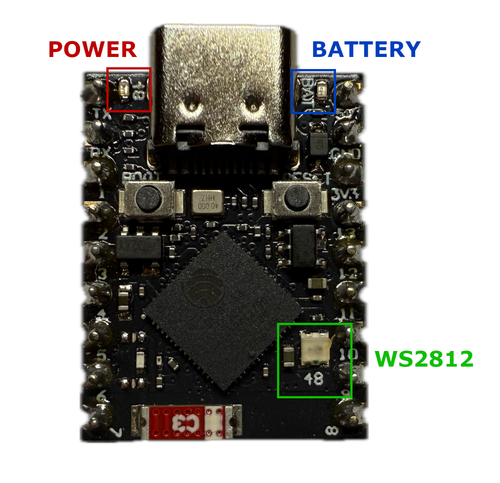

The ESP32-S3 Supermini features multiple onboard LEDs, each mapped to specific GPIO pins. Below is a breakdown of their functions, pin assignments, and how to use them in both Arduino and ESPHome.
🔴 Red LED – Power Indicator
- GPIO:
GPIO48 - Control:
digitalWrite() - ⚠️ Both the Red LED and WS2812 share GPIO48 and use different signal types (digital vs. timing-based), but due to the board’s fixed hardware design, they cannot be used independently - any signal sent to GPIO48 will affect both, potentially causing flickering or unexpected behavior.
void setup() {
pinMode(48, OUTPUT);
}
void loop() {
digitalWrite(48, HIGH);
delay(1000);
digitalWrite(48, LOW);
delay(1000);
}
output:
- platform: gpio
pin: 48
id: red_led
light:
- platform: binary
name: "Red LED"
output: red_led
🔵 Blue LED – Battery Charge Indicator
- GPIO:
None - Control: None
- Behavior:
- ⚡ Charging → LED on
- ✅ Battery connected → LED off
- 🔋 No battery → LED blinks
🌈 WS2812 LED – Programmable RGB
- GPIO:
GPIO48 - Control: FastLED, NeoPixel, etc.
- ⚠️ Both the Red LED and WS2812 share GPIO48 and use different signal types (digital vs. timing-based), but due to the board’s fixed hardware design, they cannot be used independently - any signal sent to GPIO48 will affect both, potentially causing flickering or unexpected behavior.
#include <FastLED.h>
#define NUM_LEDS 1
#define DATA_PIN 48
CRGB leds[NUM_LEDS];
void setup() {
FastLED.addLeds<NEOPIXEL, DATA_PIN>(leds, NUM_LEDS);
}
void loop() {
leds[0] = CRGB::Red; FastLED.show(); delay(1000);
leds[0] = CRGB::Green; FastLED.show(); delay(1000);
leds[0] = CRGB::Blue; FastLED.show(); delay(1000);
}light:
- platform: neopixelbus
type: GRB
pin: 48
num_leds: 1
name: "Onboard RGB LED"Useful Links
Datasheets and resources for ESP32-S3 Super Mini
ESP32-S3 Super Mini Custom Pin Mapping
Pin configuration and GPIO mapping for ESP32-S3 Super Mini
| Pin | Function | ESP Pin | I/O Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 5V | 5V | POWER INPUT | 5V power input for the board |
| 2 | GND | GND | POWER GROUND | Ground connection |
| 3 | 3V3 | 3.3V | POWER OUTPUT | 3.3V power output for peripherals |
| 4 | TX | TX | TX | TX |
| 5 | RX | RX | RX | RX |
| 6 | IO1 | GP1 | BIDIRECTIONAL | GPIO, ADC Pin |
| 7 | IO2 | GP2 | BIDIRECTIONAL | GPIO, ADC pin |
| 8 | IO3 | GP3 | BIDIRECTIONAL | GPIO, ADC pin |
| 9 | IO4 | GP4 | BIDIRECTIONAL | GPIO, ADC pin |
| 10 | IO5 | GP5 | BIDIRECTIONAL | GPIO, ADC pin |
| 11 | IO6 | GP6 | BIDIRECTIONAL | GPIO, ADC pin |
| 12 | IO7 | GP7 | BIDIRECTIONAL | GPIO, ADC pin |
| 13 | IO8 | GP8 | BIDIRECTIONAL | GPIO, ADC pin |
| 14 | IO9 | GP9 | BIDIRECTIONAL | GPIO, ADC pin |
| 15 | IO10 | GP10 | BIDIRECTIONAL | GPIO, ADC pin |
| 16 | IO11 | GP11 | BIDIRECTIONAL | GPIO, ADC pin |
| 17 | IO12 | GP12 | BIDIRECTIONAL | GPIO, ADC pin |
| 18 | IO13 | GP13 | BIDIRECTIONAL | GPIO, ADC pin |
| 19 | IO14 | GP14 | BIDIRECTIONAL | GPIO, ADC pin |
| 20 | IO15 | GP15 | BIDIRECTIONAL | GPIO, ADC pin |
| 21 | IO16 | GP16 | BIDIRECTIONAL | GPIO, ADC pin |
| 22 | IO17 | GP17 | BIDIRECTIONAL | GPIO |
| 23 | IO18 | GP18 | BIDIRECTIONAL | GPIO |
| 24 | IO21 | GP21 | BIDIRECTIONAL | GPIO |
| 25 | IO33 | GP33 | BIDIRECTIONAL | GPIO |
| 26 | IO34 | GP34 | BIDIRECTIONAL | GPIO |
| 27 | IO35 | GP35 | BIDIRECTIONAL | GPIO |
| 28 | IO36 | GP36 | BIDIRECTIONAL | GPIO |
| 29 | IO37 | GP37 | BIDIRECTIONAL | GPIO |
| 30 | IO38 | GP38 | BIDIRECTIONAL | GPIO |
| 31 | IO39 | GP39 | BIDIRECTIONAL | GPIO |
| 32 | IO40 | GP40 | BIDIRECTIONAL | GPIO |
| 33 | IO41 | GP41 | BIDIRECTIONAL | GPIO |
| 34 | IO45 | GP45 | BIDIRECTIONAL | GPIO |
| 35 | IO46 | GP46 | BIDIRECTIONAL | GPIO |
| 36 | IO47 | GP47 | BIDIRECTIONAL | GPIO |
| 37 | IO48 | GP48 | BIDIRECTIONAL | GPIO |
Pin Mappings
Complete pinout and GPIO mapping for ESP32-S3 Super Mini
| Pin | Analog | Touch | PWM | Other |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | A0 | |||
| 1 | A1 | |||
| 2 | A2 | |||
| 3 | A3 | |||
| 4 | A4 | SCK | ||
| 5 | A5 | MISO | ||
| 6 | MOSI | |||
| 7 | SS | |||
| 8 | WS2812_RGB SDA | |||
| 9 | SCL | |||
| 20 | RX | |||
| 21 | TX |
Default Tools & Configuration
Build and upload settings for ESP32-S3 Super Mini
| Setting | Value |
|---|---|
| Bootloader tool | esptool_py |
| Uploader tool | esptool_py |
| Network uploader tool | esp_ota |
| Bootloader address | 0x0 |
| Flash mode | qio |
| Boot mode | qio |
| Maximum upload size | 1280 KB (1310720 bytes) |
| Maximum data size | 320 KB (327680 bytes) |
The ESP32-S3 Super Mini uses esptool_py for uploads , esp_ota for OTA updates, and esptool_py bootloader at 0x0.
Flash mode: qio | Boot mode: qio
Max sketch size: 1280 KB | Max data size: 320 KB
Similar Boards
Other development boards with ESP32S3 microcontroller
UM PROS3
UM PROS3 development board is based on esp32s3 microcontroller and uses xtensa architecture.

Espressif ESP32-S3-Korvo-1
Espressif ESP32-S3-Korvo-1 development board is based on esp32s3 microcontroller and uses xtensa architecture.

ESP32-S3-USB-OTG
ESP32-S3-USB-OTG development board is based on esp32s3 microcontroller and uses xtensa architecture.