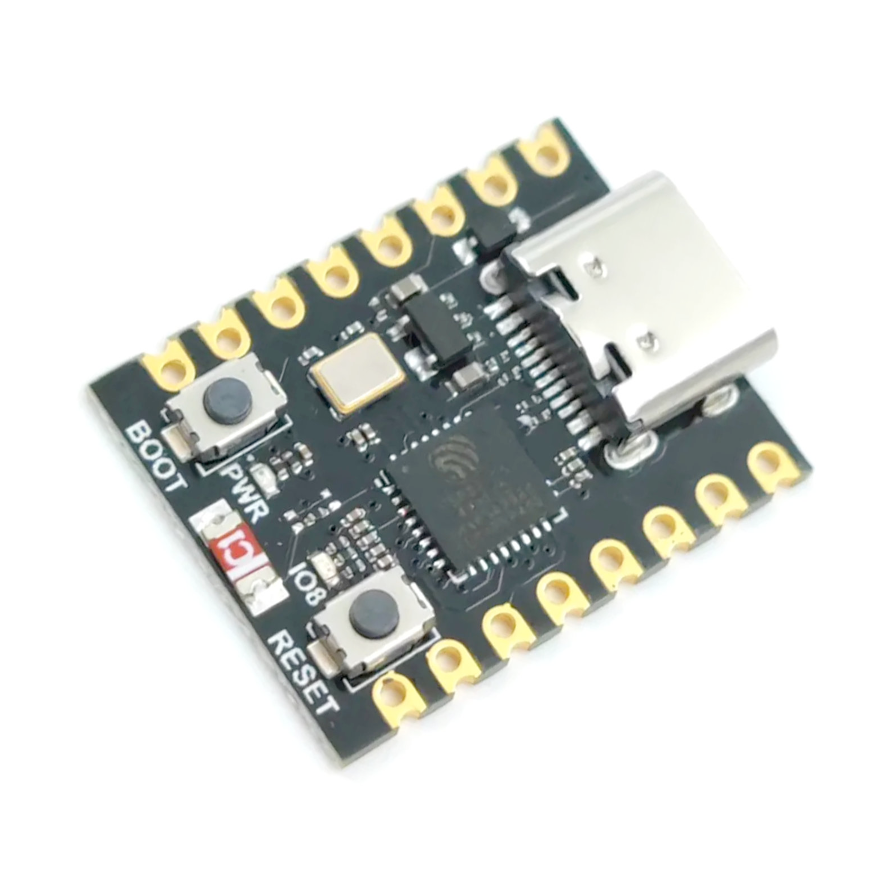
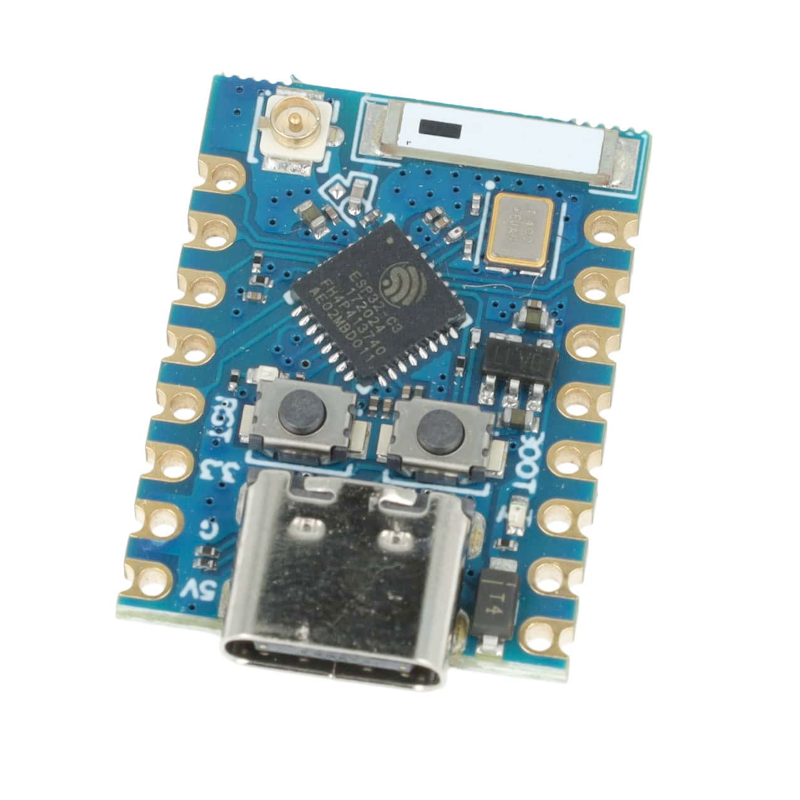
ESP32S3 Walter Module Development Board
Code name: ESP32S3_DEV
ESP32S3 Walter Module development board is based on esp32s3 microcontroller and uses xtensa architecture. This board has a maximum CPU frequency of 240 MHz and a flash size of 16MB.
About ESP32S3 Walter Module
Walter is a small, highly integrated IoT module built to tackle complex connectivity and processing needs. At its core is the ESP32-S3, a versatile system-on-chip (SoC) featuring a dual-core processor with hardware acceleration for machine learning, cryptography, and signal processing. It includes a range of peripherals, such as UART, SPI, I²C, and CAN, alongside built-in Wi-Fi b/g/n and Bluetooth 5, providing robust local networking and communication options.
What sets Walter apart is its inclusion of the Sequans GM02SP modem, offering LTE-M and NB-IoT 5G connectivity for low-power, wide-area communication, ideal for IoT applications. The modem also integrates a GNSS receiver, adding precise positioning capabilities for tasks like asset tracking, navigation, or geolocation.
Technical Specifications
🛰️ Connectivity
🧠 Microcontroller
✨ Features
- LTE: CAT M1/NB1/NB2 (GM02SP module)
- GPS: GPS, GNSS Constellation support (GM02SP module)
- Ultra low deep sleep current of 9.8µA
- Certified for CE, FCC, IC, UKCA, New-Zealand and Australia
- 24 digital IO pins
- 22 external interrupt pins
- 22 analog input pins
- 22 PWM pins
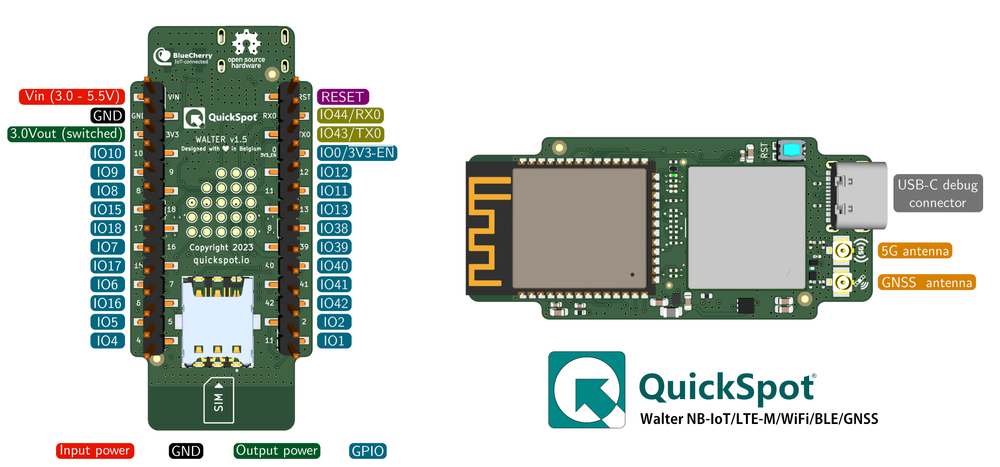
ESP32S3 Walter Module Pinout
✅ Safe Pins to Use
For general GPIO usage, these are the safest and most flexible choices:
Why Are These Pins Safe?
- Not involved in bootstrapping → No impact on device boot mode or system startup
- Not linked to flash memory or PSRAM → Won't interfere with storage or memory access
- Not dedicated to USB or JTAG → Free for general use without affecting debugging
- No special hardware connections → Freely assignable without internal conflicts
⚠️ Pins to Avoid or Use with Caution
Some pins are reserved for critical functions like bootstrapping, JTAG debugging, USB communication, and flash memory operations. Misusing these pins may lead to boot failures, programming issues, USB conflicts, or disruptions in flash storage.
Critical Pin Categories:
- 🛠️ Strapping Pins: Control boot behavior and flash voltage selection
- 🔗 JTAG Debugging Pins: Required for low-level debugging
- 🔌 USB Communication Pins: Used for USB Serial/JTAG communication
- ⚡ Flash Memory & SPI Pins: Connected to SPI flash memory and PSRAM
- 📡 UART Serial Communication Pins: Used for debugging and firmware uploads
| PIN | Label | Reason | Function |
|---|---|---|---|
| IO12 | FSPICLK | Drives the flash (and PSRAM) clock. This critical signal must be reserved for memory and not used as general GPIO. | ⚡ Flash |
| IO11 | FSPID | Used as a data line for flash (and in-package PSRAM). It should not be used as GPIO when the flash/PSRAM is in use. | ⚡ Flash |
| IO13 | FSPIQ | Used as a data line for flash/PSRAM transfers. Not available for other uses when flash/PSRAM is connected. | ⚡ Flash |
| IO38 | FSPIWP | On flash-equipped chips, this pin is tied to the flash’s WP# (or D3) line. It should be avoided for other use, as it’s needed for flash operations. | ⚡ Flash |
| IO39 | MTCK (GPIO39) | Default JTAG debugging TCK pin. If JTAG is needed, this pin must be free; it may also be used internally for PSRAM chip select on certain modules, so avoid repurposing it. | 🪛 Other |
ESP32S3 Walter Module Pin Mappings
This development board provides 24 digital IO pins, out of which 22 can be used as external interrupt pins , 22 as analog input pins and 22 pins have Pulse-Width Modulation (PWM) .
| Pin | Function | ESP Pin | Input/Output | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | RESET | EN | input | ESP32 reset with 10k pullup |
| 2 | IO44/RX0 | RXD0 | bidirectional | ESP32 UART0 Receive |
| 3 | IO43/TX0 | TXD0 | bidirectional | ESP32 UART0 Transmit |
| 4 | DFU/3V3 EN | IO0 | bidirectional | DFU when low on boot and 3V3 output enable |
| 5 | IO12 | IO12 | bidirectional | General purpose I/O |
| 6 | IO11 | IO11 | bidirectional | General purpose I/O |
| 7 | IO13 | IO13 | bidirectional | General purpose I/O |
| 8 | IO38 | IO38 | bidirectional | General purpose I/O |
| 9 | IO39 | IO39 | bidirectional | General purpose I/O |
| 10 | IO40 | IO40 | bidirectional | General purpose I/O |
| 11 | IO41 | IO41 | bidirectional | General purpose I/O |
| 12 | IO42 | IO42 | bidirectional | General purpose I/O |
| 13 | IO2 | IO2 | bidirectional | General purpose I/O |
| 14 | IO1 | IO1 | bidirectional | General purpose I/O |
| 15 | IO4 | IO4 | bidirectional | General purpose I/O |
| 16 | IO5 | IO5 | bidirectional | General purpose I/O |
| 17 | IO6 | IO6 | bidirectional | General purpose I/O |
| 18 | IO7 | IO7 | bidirectional | General purpose I/O |
| 19 | IO15 | IO15 | bidirectional | General purpose I/O |
| 20 | IO16 | IO16 | bidirectional | General purpose I/O |
| 21 | IO17 | IO17 | bidirectional | General purpose I/O |
| 22 | IO18 | IO18 | bidirectional | General purpose I/O |
| 23 | IO8 | IO8 | bidirectional | General purpose I/O |
| 24 | IO9 | IO9 | bidirectional | General purpose I/O |
| 25 | IO10 | IO10 | bidirectional | General purpose I/O |
| 26 | 3V3 OUT | N/A | power output | Switchable 3.3VDC output |
| 27 | GND | GND | power ground | GND connection |
| 28 | VIN | N/A | power input | DC Power input port |
Default Tools
| Bootloader tool | esptool_py |
| Uploader tool | esptool_py |
| Network uploader tool | esp_ota |
| Bootloader address | 0x0 |
| Flash mode | dio |
| Boot mode | qio |
| PSRAM type | qspi |
The ESP32S3 Walter Module development board by default uses esptool_py uploader tool, esp_ota network uploader tool for Over-the-air (OTA) uploads and esptool_py bootloader tool. The bootloader starts at address "0x0". Flash mode and boot mode for ESP32S3 Walter Module development board by default is dio and qio respectively. The board uses qspi PSRAM type.