ESP32 GY-530 VL53L0X Time-of-Flight Sensor Pinout, Wiring and more
Overview
The GY-530 is a breakout board for the VL53L0X Time-of-Flight (ToF) sensor from STMicroelectronics. It uses FlightSense technology to measure distances up to 2 meters with 1mm resolution and includes onboard level shifting and voltage regulation, making it compatible with 3.3V and 5V microcontrollers.
Choose Your Platform
About GY-530 VL53L0X Time-of-Flight Sensor
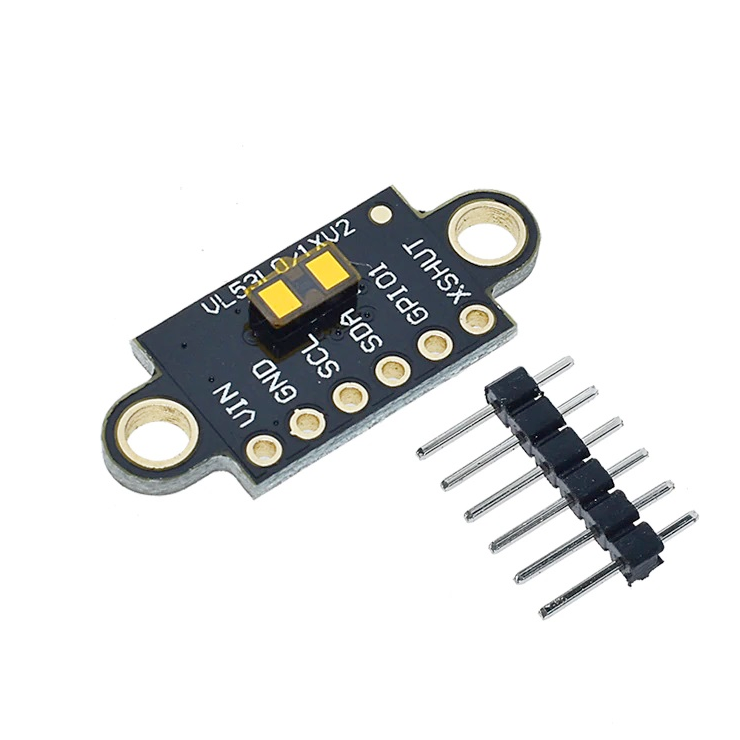
📏 GY-530 Sensor Overview
- Sensor: VL53L0X (STMicroelectronics)
- Range: 3cm to 200cm (max), with 1mm resolution
- Interface: I²C (with level shifters)
- Operating Voltage: 2.6V to 5.5V (via VIN)
- Board Size: ~20mm x ~15mm
- Colors: Available in both blue and purple PCBs - functionally identical
- Additional Pins: XSHUT (shutdown) and VDD (2.8V regulator output)
Check Other sensors modules based on VL53L0X Time of Flight Sensor:
Where to Buy GY-530 VL53L0X Time-of-Flight Sensor



Prices are subject to change. We earn from qualifying purchases as an Amazon Associate.
GY-530 Datasheet and Technical Specifications
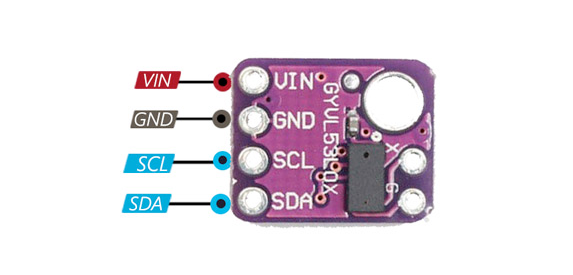
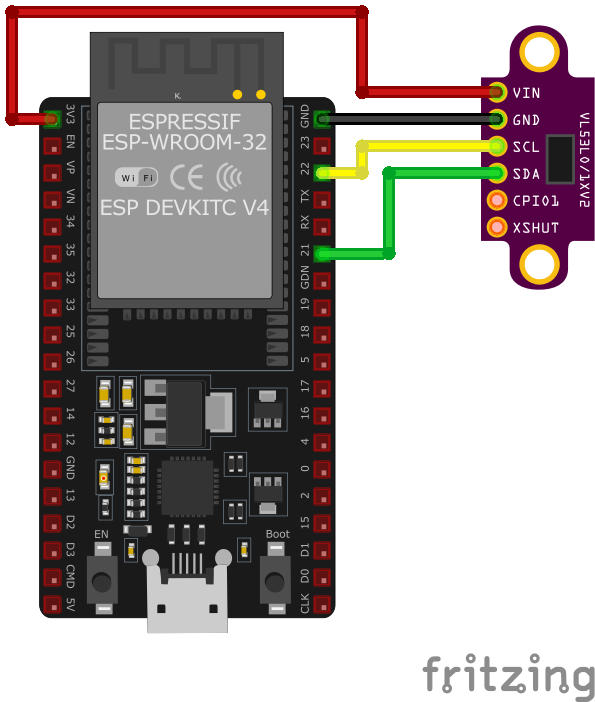
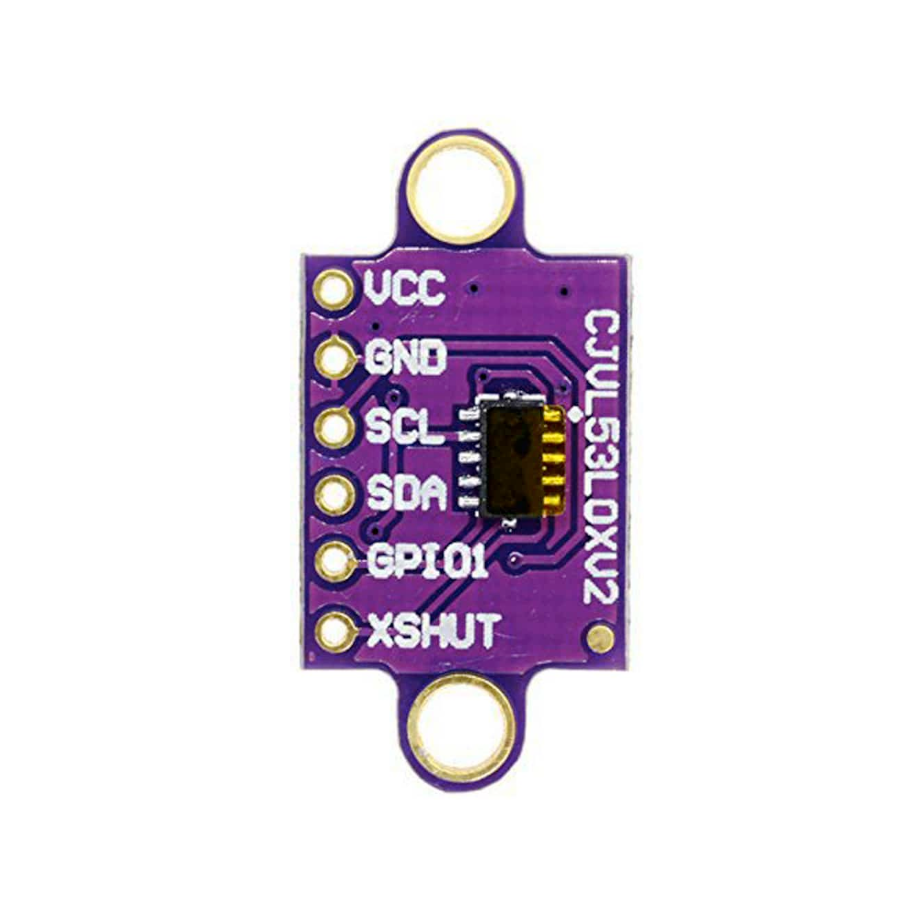
GY-530 Pinout Diagram
The VCC pin is used to supply power to the sensor,
and it typically requires 3.3V or 5V (refer to the datasheet for specific voltage requirements).
The GND pin is the ground connection and must be
connected to the ground of your ESP32.
- VIN: 2.6V–5.5V power input
- GND: Ground
- SCL: I²C Clock (level-shifted to VIN)
- SDA: I²C Data (level-shifted to VIN)
- XSHUT: Active-low shutdown (not level-shifted)
- VDD: 2.8V output from onboard regulator (can also be used as input if VIN is disconnected)
GY-530 Troubleshooting Guide
Common Issues
🛑 No I²C Address Detected
Issue: GY-530 not showing up on I²C scanner.
Solution: Ensure SDA/SCL are properly connected and powered, and that XSHUT is not held LOW.
📉 Poor Accuracy or Fluctuating Readings
Issue: Distance values jump around or seem wrong.
Solution: Check for surface reflectivity issues, increase timing budget, or average multiple readings.
⚠️ Sensor Keeps Resetting
Issue: Unstable readings or sensor dropping off I²C bus.
Solution: Use a stable 3.3V or 5V supply. Avoid floating XSHUT pin - tie it high if unused.
Debugging Tips
🔍 Serial Monitor
Use the Serial Monitor to check for error messages and verify the sensor's output. Add debug prints in your code to track the sensor's state.
⚡ Voltage Checks
Use a multimeter to verify voltage levels and check for continuity in your connections. Ensure the power supply is stable and within the sensor's requirements.
Additional Resources
GY-530 Code Examples
Arduino Example
#include <Wire.h>
#include <Adafruit_VL53L0X.h>
Adafruit_VL53L0X lox = Adafruit_VL53L0X();
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
Wire.begin();
if (!lox.begin()) {
Serial.println("Failed to initialize GY-530 VL53L0X sensor!");
while (1);
}
Serial.println("GY-530 ready!");
}
void loop() {
VL53L0X_RangingMeasurementData_t measure;
lox.rangingTest(&measure, false);
if (measure.RangeStatus != 4) {
Serial.print("Distance: ");
Serial.print(measure.RangeMilliMeter);
Serial.println(" mm");
} else {
Serial.println("Out of range");
}
delay(500);
}ESPHome Example
i2c:
sda: 21
scl: 22
sensor:
- platform: vl53l0x
name: "GY-530 Distance"
update_interval: 1sMicroPython Example
from machine import I2C, Pin
import time
import vl53l0x
i2c = I2C(0, scl=Pin(22), sda=Pin(21))
tof = vl53l0x.VL53L0X(i2c)
tof.start()
while True:
print("Distance:", tof.read(), "mm")
time.sleep(0.5)vl53l0x.py driver to read and print distance values.
Conclusion
The ESP32 GY-530 VL53L0X Time-of-Flight Sensor is a powerful distance sensor that offers excellent performance and reliability. With support for multiple development platforms including Arduino, ESP-IDF, ESPHome, PlatformIO, and MicroPython, it's a versatile choice for your IoT projects.
For optimal performance, ensure proper wiring and follow the recommended configuration for your chosen development platform.
Always verify power supply requirements and pin connections before powering up your project to avoid potential damage.